Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×






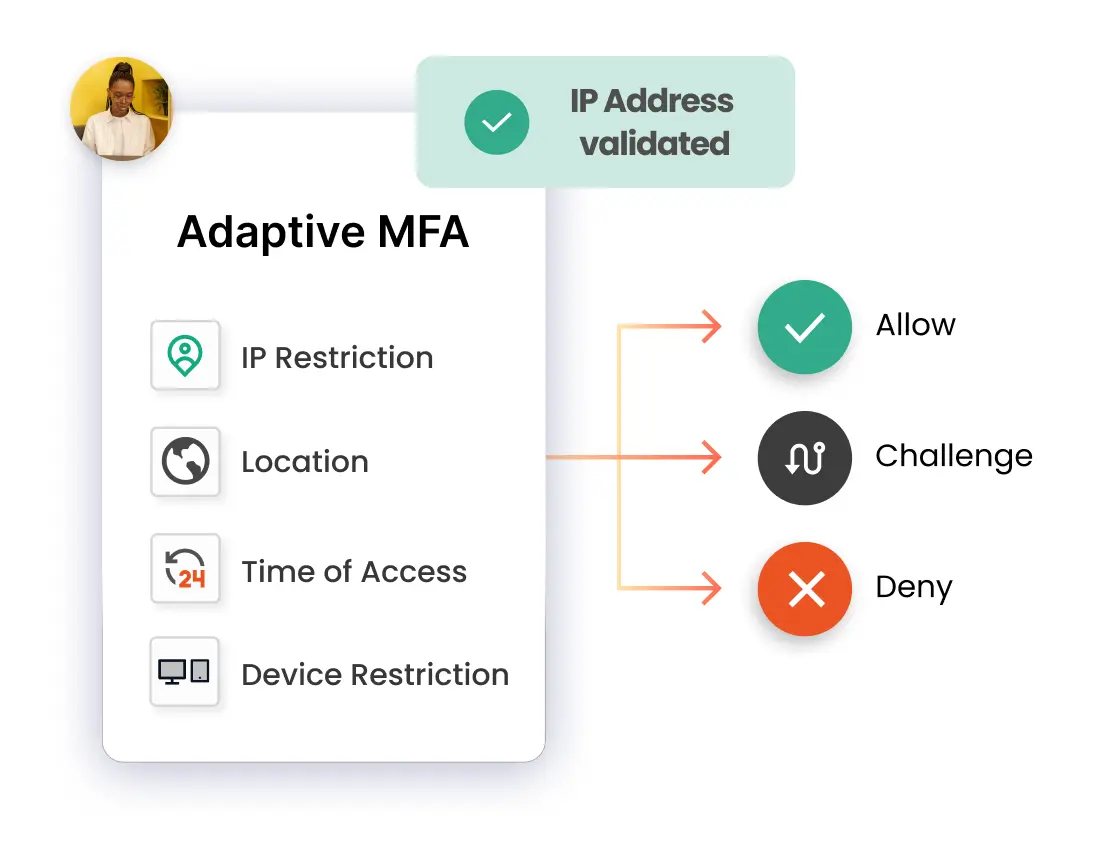
Ensure proactive, continuous protection against cybersecurity threats with Adaptive MFA features.
This evaluates context in real-time for every login, reacting instantly to high-risk activity while keeping the login experience smooth for known users.
Easily deploy the Adaptive MFA product to any device (tablets, laptops, desktops, or mobiles) that supports a web browser, regardless of operating system.
Recognizes the devices users usually log in from by analyzing attributes such as OS, hardware, IP, location, etc. A login from an unfamiliar device raises the risk level and triggers stronger authentication.
A risk score shows how risky a login is (low, medium, or high) based on factors like device, IP, time, location, and behavior. No extra factor for low risk, extra verification for medium risk, and denial of access for high‑risk attempts.
IT teams define clear “if-this-then-that” rules that use conditions like role, location, device trust, time, IP risk, etc., to decide whether to allow, enforce MFA, or block access.
This feature learns habits and behavior of a user, understands the usual devices used, login time, and locations. When something doesn’t match the normal pattern, then it adds extra checks or blocks access.
miniOrange Adaptive Authentication secures the business applications your teams rely on with intelligent, context-aware access control. By evaluating device trust, location, and user behavior in real time, it ensures seamless access for trusted users and stronger verification when risk increases. From productivity suites to enterprise platforms, miniOrange protects access without disrupting workflows.
Explore miniOrange app Integration Catalog







Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication adjusts security based on how risky a login or action looks. When risk is high, it adds extra checks like biometrics or OTPs; when risk is moderate, it applies lighter verification; and when risk is low, users get smooth, low-friction access. The steps are explained below:
The user attempts to log in or perform an action (e.g., logging in, making a transaction) on a system or application.
The system performs a risk-based authentication assessment by analyzing various factors such as
The process verifies and approves new or unrecognized devices so that only trusted devices can log into a network or system.
The user provides the required authentication factors as requested by the system.
If the user successfully completes the required authentication steps, they are granted access.

Check out Adaptive MFA Demo to see how you can enable risk-based authentication for your applications.
View Demo*Please contact us to get volume discounts for higher user tiers.
When using IP Restriction as risk-based authentication, IP addresses are configured and enlisted by the admin, and access is either allowed or denied accordingly. When a user attempts to log into one of the risk-based authentication-enabled apps, his IP address is checked against the preset IP list, and appropriate action is taken (i.e., Allow, Deny, or Challenge).
In Location-based Risk-Based Authentication restriction, the admin shortlists and configures a list of Geo-locations. Based on the location restrictions set by the admin, end-users are either allowed or denied the login. When a user tries to log in with Risk-Based Authentication enabled, his location attributes are verified against the location list configured by the admin, and based on this, the user will be either allowed, challenged, or denied access to resources.
Using Device-based Risk-Based Authentication, the admin allows end-users to add a set number of trusted devices (A device refers to a Browser Session). A registered device allows a person to log in without restriction once it has been registered. An administrator will challenge or deny a person's registration if their registered device exceeds their total limit.
Risk-Based Authentication also includes a time restriction, which starts with an admin setting up a time zone with a Start and End Time. Users are permitted, refused, or challenged based on the defined timezone and policies. As soon as an end-user attempts to log in with risk-based authentication enabled, his time zone parameters, such as time zone and system time, are compared to the list defined by the admin, and the user is either granted access, rejected access, or challenged access, depending on his configuration.
Adaptive MFA strengthens security by dynamically analyzing risk signals (location, device, time, user behavior, etc.) and triggering additional authentication steps only when suspicious activity is detected.
Dynamically adjusts security checks based on contextual aspects such as location, device, or IP address, and authenticates every access request, not just at login, but throughout the user’s session.
Home and public networks often lack enterprise-grade protections, making remote users a prime target for threats. So, dynamic work cultures make it essential to verify every access attempt to protect resources.
Google Workspace Security to protect Gmail, Drive, & other Workspace apps by prompting Adaptive MFA only when risk signals appear. Also, protect high-value workloads like Exchange Online, SharePoint, Teams, & admin portals with strong verification.
Add Adaptive MFA to the VPN network for secure remote access with 15+ authentication methods. For example, if a user attempts VPN access from a new location at odd hours, MFA challenges kick in while regular logins stay friction‑free.
Prevent cyberattacks on apps like Salesforce, Slack, or Dropbox with an SSO and MFA solutions. For example, if login behavior deviates from the norm (e.g., sudden access from multiple devices), Adaptive MFA requests extra verification across all connected apps.





I can't speak highly enough regarding miniOrange, I am totally satisfied with the process and results in every regard.
5.0

Awesome tech service, Awesome product. Overall Awesome people. This solution is very simple and easy to implement
5.0
