Active Directory Single Sign-On (AD SSO) is a powerful authentication mechanism designed to enhance user experience while enhancing organizational security. By enabling users to log in once and gain access to multiple applications and systems seamlessly, AD SSO eliminates the need for repetitive credential entry across different platforms.
This technology leverages Active Directory, a widely used directory service, to streamline access to business applications and IT systems, both internal and third-party. Not only simplifies the login process for employees and external users, but it also aligns with modern identity and access management (IAM) strategies, which prioritize efficiency, security, and a better user experience.
AD SSO plays a critical role in reducing password fatigue, enhancing productivity, and improving overall security by integrating seamlessly into broader Zero Trust frameworks. For businesses seeking to unify access while maintaining stringent security controls, AD SSO offers a robust solution. This guide will dive deeper into how it works, its benefits, and its relevance in today’s dynamic IT environments.
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It serves as a central hub for managing network resources, enabling administrators to set up and control permissions and access to networked resources. AD is primarily used to authenticate and authorize users and computers in a Windows domain type network, assigning and enforcing security policies for all computers and installing or updating software across a network.
For organizations expanding beyond on-premises infrastructure, Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) extends these capabilities to the cloud. Azure AD provides seamless single sign-on to both cloud and on-premises applications, supports a variety of devices including iOS, macOS, Android, and Windows, and enhances security with integrated multi-factor authentication. This integration allows businesses to maintain a consistent identity across their on-premises and cloud environments, simplifying user management while enhancing data security.
What is AD SSO?
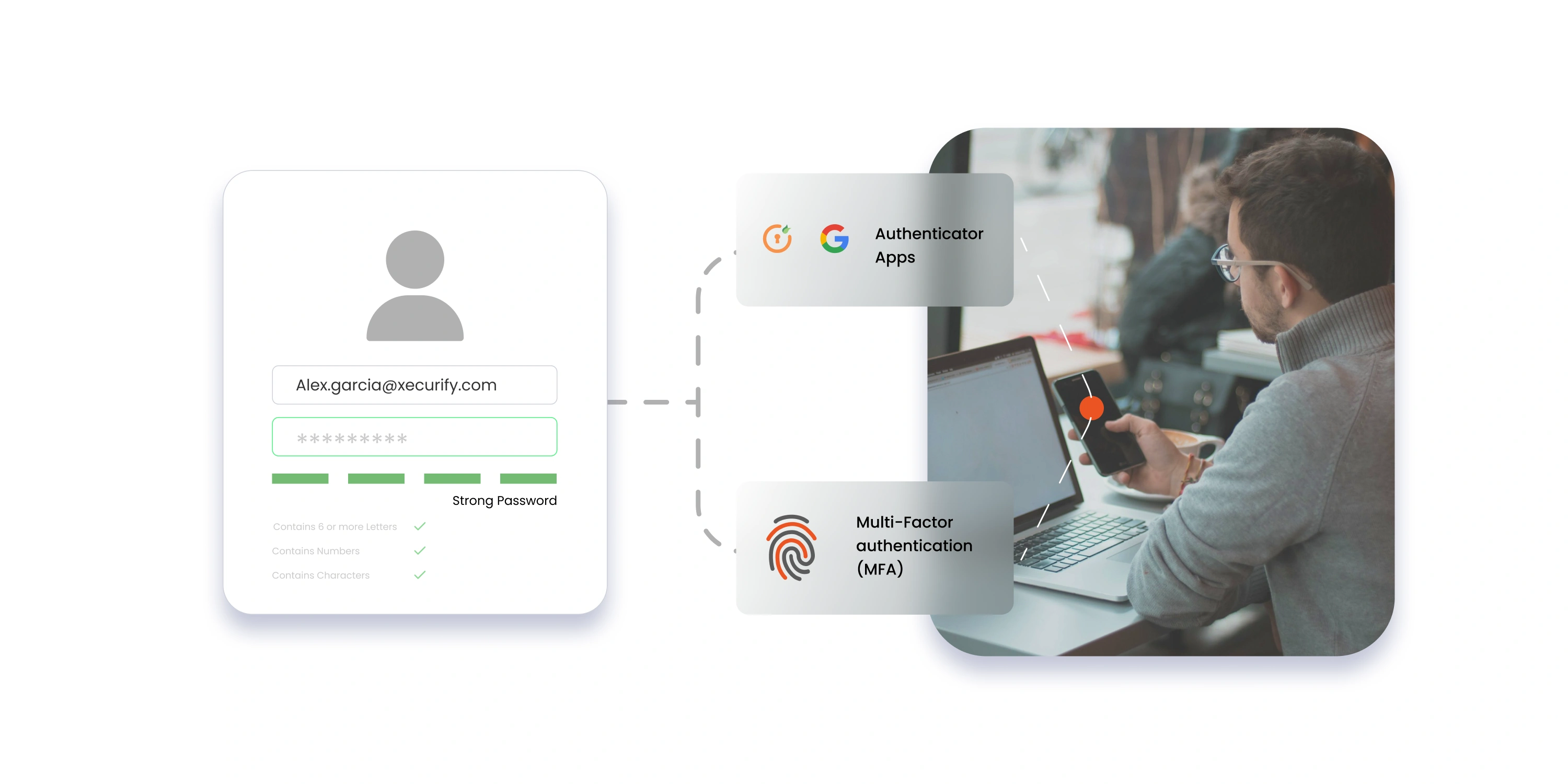
Active Directory Single Sign-On (AD SSO) is a feature within Microsoft's directory services that simplifies the user authentication process across multiple applications. With AD SSO, users can log in once with a single set of login credentials, granting them access to a range of applications and services without the need to sign in again for each one separately. This is accomplished through the creation and validation of access tokens. When a user first logs in, AD generates an access token, a digital key that grants permission to the suite of applications they are authorized to access. This token is stored locally on the user's device and is checked each time the user accesses a new application, seamlessly validating their credentials.
5 Key Benefits of AD SSO
1. Seamless Integration with Applications
AD SSO effortlessly integrates with a wide range of applications, enabling users to access the tools and resources they need without the hassle of repeated logins. This compatibility ensures smooth functionality across enterprise ecosystems.
2. Simplified User Access
By centralizing authentication, AD SSO streamlines user access, allowing employees to log in just once and get access to all authorized applications. This reduces disruptions and boosts productivity.
3. Enhanced Security
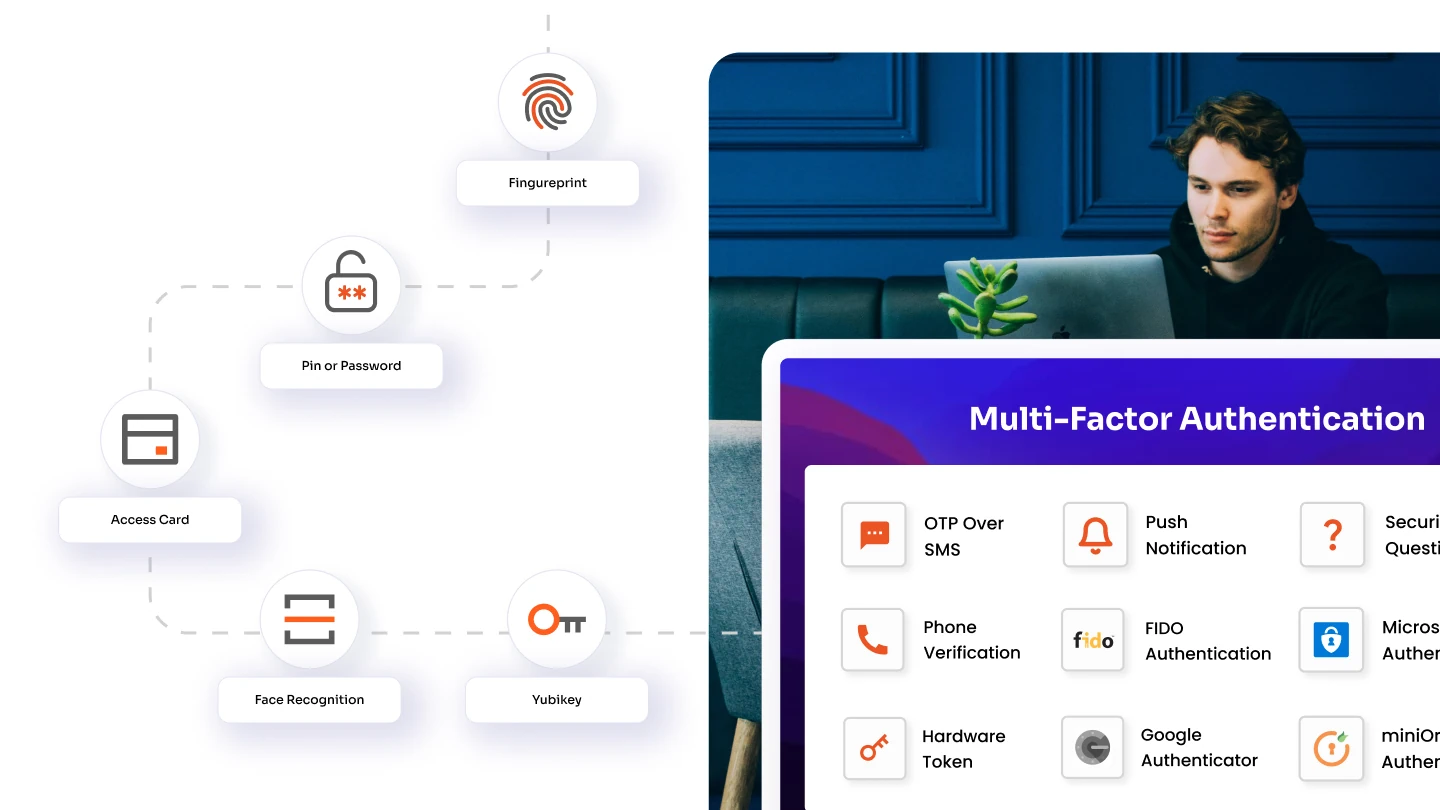
AD SSO minimizes the risks associated with multiple login attempts. Features like multi-factor authentication (MFA), add an additional layer of security, ensuring that sensitive data and applications are well-protected, even if credentials are compromised.
4. Reduced Password Fatigue
Users no longer need to remember or manage multiple passwords, reducing the likelihood of weak or reused credentials. This improvement not only enhances security but also improves the user experience by eliminating unnecessary password-related frustrations.
5. Streamlined IT Management
AD SSO simplifies IT operations by reducing the need for password resets and other login-related issues. This allows IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine administrative tasks, leading to more efficient management.
How to Set Up Azure AD SSO
Setting up Single Sign-On (SSO) with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) simplifies user access to applications while enhancing security. Follow these steps to configure Azure AD SSO effectively:
Step 1: Prepare Your Environment
Before enabling SSO, ensure the necessary prerequisites are in place to support seamless integration:
- Set up the Azure AD Connect server and ensure it supports the required network configuration.
- Acquire domain administrator credentials for configuration.
- Enable the modern authentication feature for your Azure AD tenant.
- Update client systems to the latest Microsoft 365 version for compatibility.
These preparations lay the foundation for a successful SSO implementation.
Step 2: Activate Seamless SSO
To enable seamless SSO, follow these steps based on your Azure AD Connect setup:
- For a Fresh Installation:
During the installation process of Azure AD Connect, choose the Custom installation option. On the User sign-in page, select Enable single sign-on to proceed with the configuration. - For an Existing Installation:
If Azure AD Connect is already installed, navigate to Change user sign-in in Azure AD Connect and click Next. For versions 1.1.880.0 and above, seamless SSO is selected by default; for older versions, you’ll need to enable it manually.
Follow the configuration wizard to the Enable single sign-on page. Provide the domain administrator credentials for each Active Directory forest synced to Azure AD via Azure AD Connect. Once the setup is complete, seamless SSO will be enabled on your tenant.
Step 3: Verify SSO Configuration
Ensure that Azure AD SSO is functioning correctly:
- Log in to the Azure AD admin center using global administrator credentials.
- Navigate to Azure Active Directory on the left menu.
- Select Azure AD Connect from the options.
- Confirm that the Seamless single sign-on field is marked Enabled.
AD SSO Protocols: SAML vs. OAuth
Active Directory (AD) Single Sign-On (SSO) uses authentication protocols like SAML and OAuth to provide seamless and secure user access to applications. These protocols differ in functionality and are suited for specific use cases, depending on the type of application and its authentication requirements.
Overview of SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language)
SAML is an XML-based protocol designed for secure and efficient user authentication and authorization. It enables identity providers (like AD) to share authentication information with service providers (applications), allowing users to log in once and access multiple applications without the need to reauthenticate. Used for apps that don’t support OAuth or OpenID Connect (OIDC). Frequently used for older or on-premises applications.
Overview of OAuth (Open Authorization)
OAuth is a modern protocol designed for authorization rather than authentication, commonly used in cloud and mobile applications. It enables users to grant limited access to applications without sharing their passwords. When combined with OpenID Connect (OIDC), OAuth supports authentication workflows as well. This is suitable for cloud-based or third-party applications. It also Allows granular access control, specifying what resources an app can access.
Choosing the Right Protocol
At last, the decision to use SAML or OAuth depends on the application’s environment and its support for authentication protocols:
- Use SAML for legacy, enterprise, or on-premises applications without OAuth support.
- Use OAuth (or OIDC) for modern, cloud-based, or third-party applications that benefit from fine-grained access control.
In conclusion, implementing AD SSO is a game-changer for organizations striving to enhance security, streamline operations, and deliver a seamless user experience. However, the complexity of setting up and managing AD SSO requires a solution that is both robust and user-friendly. This is where miniOrange steps in.
With its expertise in identity and access management, miniOrange simplifies the deployment of AD SSO, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of applications and protocols like SAML, OAuth, and OIDC. Beyond technical integration, miniOrange provides enhanced security features such as multi-factor authentication and session monitoring to align with your organization's Zero Trust framework. Partner with miniOrange to make your AD SSO implementation not just effective but transformative for your business. Let us help you secure, simplify, and scale your access management today.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between AD SSO and Azure AD SSO?
AD SSO (Active Directory Single Sign-On) majorly works within on-premises networks to manage user access to network resources. On the other hand, Azure AD SSO is designed for cloud services, providing SSO access to a wide range of web-based applications from anywhere.
2. How does SAML SSO work with Active Directory?
SAML SSO for Active Directory allows users to log in once and access multiple services without re-entering credentials. It connects AD with other SAML-compliant services, using AD as the identity provider to authenticate and authorize user access across different platforms securely.
3. Can AD SSO be used with non-Windows platforms?
Yes, AD SSO can be used with non-Windows platforms. It integrates with various systems and applications across different operating systems, such as macOS and Linux, allowing seamless user authentication and access management across diverse environments.
Author



Leave a Comment