Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions are essential for modern organizations, offering tools to secure sensitive data and systems access. However, with robust solutions like PAM (Privileged Access Management), MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), and SSO (Single Sign-On), understanding these capabilities and their relevance can be a challenging task. This blog aims to explain IAM capabilities, helping you grasp their significance, assess your organization’s needs, and choose the right solution to safeguard your digital assets effectively.
Top IAM Capabilities
Following are the top identity and access management capabilities -
1. Identity Management
Identity management is essential for implementing any successful Identity and Access Management (IAM) framework. It simplifies the complex process of managing user identities by centralizing them into a single repository. This centralization allows for automated synchronization with an organization’s various systems and services, facilitating seamless updates and ensuring consistency across all platforms. Integrating systems examples, such as HR databases, which hold critical employee information, automates the configuration process, enhancing operational efficiency and security measures across the organization.
Key Benefits:
- Automated User Data Synchronization: Automatically updates user information across all systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Enhanced Security: Centralized management of identities helps maintain high security and compliance standards by consistently applying accurate and updated user information across all access points.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces administrative overhead and the costs associated with managing multiple systems independently, providing a streamlined approach to identity management.
- Complex Integration Needs: Requires significant effort to integrate various organizational systems and ensure they work cohesively, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
- Legacy System Challenges: Organizations relying on outdated methods may find the transition difficult, as it involves overcoming the limitations of older systems that are often slow and prone to errors.
2. Access Management
Access Management is a critical component of any Identity and Access Management (IAM) framework, focusing on determining if a user is authorized to access a specific resource. Like Identity Management, Access Management also benefits from centralization within an IAM solution, simplifying the administration of user permissions and services. Most organizations adopt Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to streamline this process, assigning access rights based on the user’s role within the organization rather than managing individual user permissions.
Key Aspects and Benefits:
- Role-Based Control: RBAC Simplifies permission management by assigning user access based on predefined roles, reducing the complexity and administrative burden of individual access rights.
- Authentication Methods: Incorporates various authentication mechanisms, such as Single Sign-On (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and passwordless options, ensuring secure and convenient access.
- Authorization Precision: Utilizes fine-grained controls like Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) and policy-based access control to tailor access rights to the specific needs and contexts of users and services.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlines user access to services, boosting productivity and ensuring faster service delivery within the organization.
- Compliance and Auditing: Supports regulatory compliance by providing transparent and traceable access management, simplifying auditing and reporting.
3. Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an essential feature of modern access management that centralizes authentication processes within an IAM solution. By enabling SSO, organizations can eliminate the need for multiple authentications by users across various services.
Key Aspects and Benefits:
- Unified Authentication: Users log in once with a single set of credentials to access all associated services, simplifying the login process and enhancing the user experience.
- Reduced IT Burden: SSO decreases the demand for IT support for password resets and account lockouts, significantly reducing helpdesk load.
- Better Security: By minimizing the number of user credentials, SSO makes it easier for users to manage and secure their login information.
- Simplified Access Management: Streamlines user access to multiple services, facilitating seamless interaction across different platforms and applications.
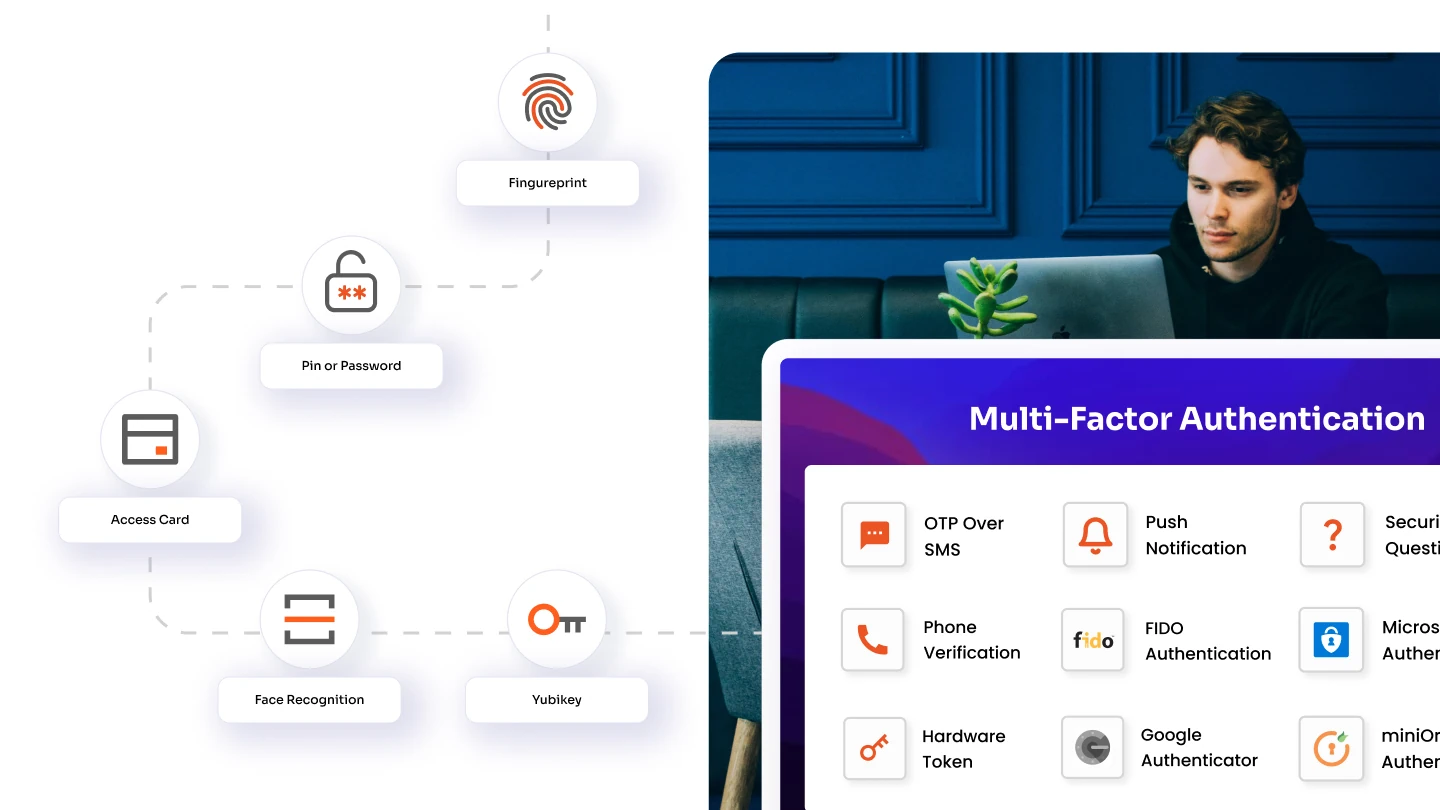
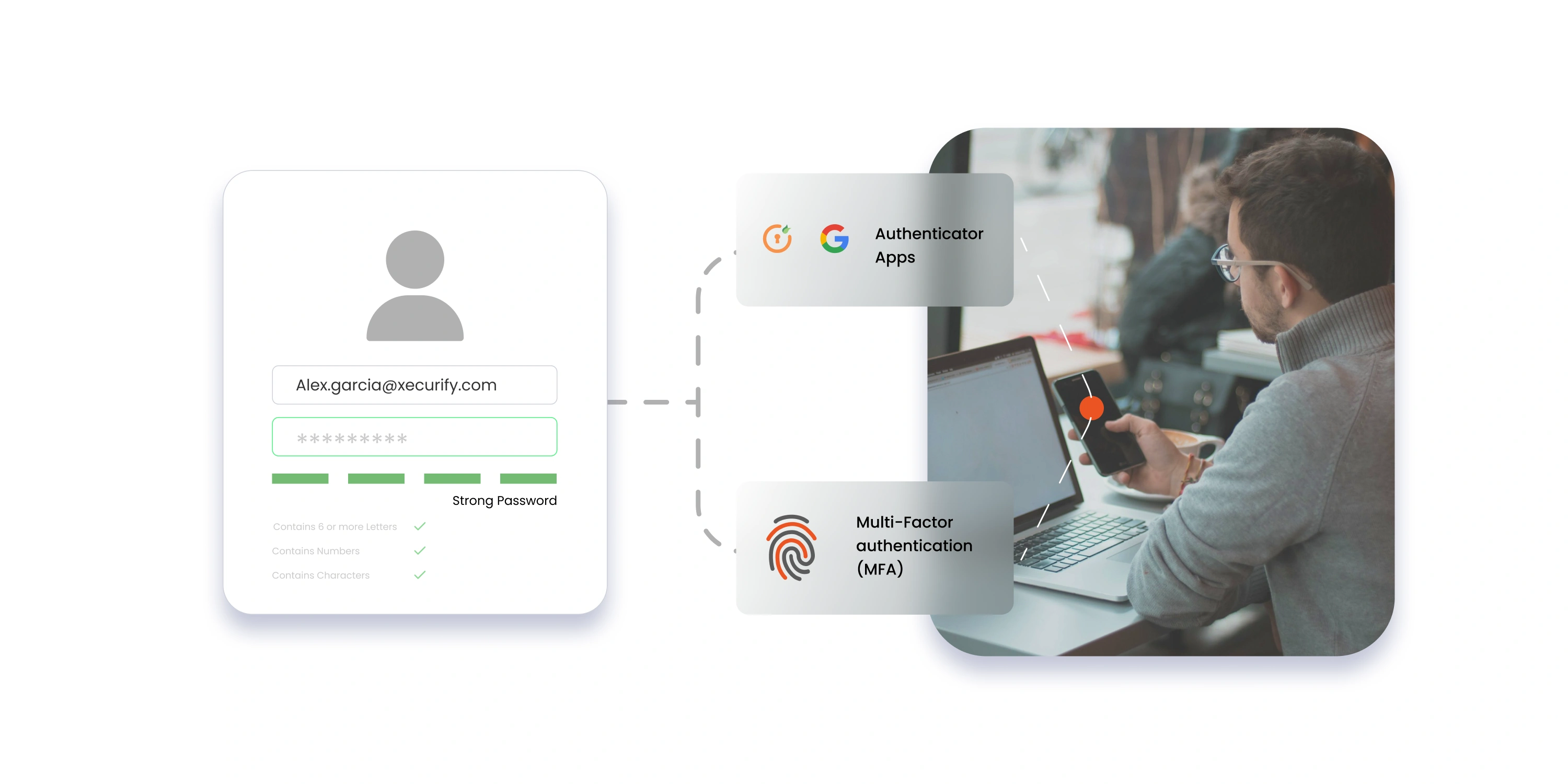
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthening Security Layers
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to the user authentication process, a crucial enhancement especially in environments utilizing SSO. MFA requires users to verify their identity using more than one method of authentication from different categories of credentials.
Key Aspects and Benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication:
- Enhanced Verification: Combines two or more independent credentials: what the user knows (password), what the user has (security token), and what the user is (biometric verification).
- Reduced Fraud Risk: Protects against unauthorized access by ensuring that the theft of one factor alone will not compromise the user's credentials.
- Flexible Security: Offers organizations the flexibility to implement tailored security requirements based on the perceived risk level of accessing sensitive information.
5. Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged Access Management (PAM) focuses on securing the access rights of highly privileged users and accounts, which are often targeted by attacks due to their elevated access rights.
Key Aspects and Benefits of Privileged Access Management:
- Enhanced Control: Provides tight control over privileged accounts by using time-limited and task-specific credentials.
- Monitoring and Detection: Continuously monitors privileged sessions and detects unauthorized or suspicious activities, enhancing security surveillance and response capabilities.
- Protects Critical Assets: Protects the organization’s most sensitive data and systems by ensuring that only authorized and authenticated users have access to critical resources.
6. Identity Governance and Administration (IGA): Streamlining Identity Lifecycle Management
Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) encompasses the comprehensive management of identity lifecycle processes across an organization. It focuses on the structured handling of user identities from their initial creation, through any changes during their association with the organization, to their eventual removal when no longer needed. This process applies not only to employees but also to guest users, machines, and customer identities.
Key Aspects and Benefits of Identity Governance and Administration:
- Lifecycle Management: Manages the complete lifecycle of identities including provisioning (creating and assigning access), updating (as roles or attributes change), and deprovisioning (removing access when no longer needed).
- Automated Processes: Utilizes technologies like SCIM (System for Cross-Domain Identity Management) and JIT (Just-In-Time) provisioning through SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) or OpenID Connect to automate and streamline these processes.
- Self-Service Capabilities: Enables users to manage aspects of their own identities, such as password resets and profile updates, enhancing user autonomy and reducing IT overhead.
- Access Governance: Focuses on auditing, logging, and analyzing identity and access data to answer critical security questions about who accessed what, when, and what actions they performed.
- Adaptive Access Policies: Implements dynamic and context-based access rules that adjust based on risk assessments, user behavior, and environmental factors to ensure secure yet flexible access controls.
The Strategic Advantages of IAM Capabilities
Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems are instrumental in enhancing organizational security and efficiency by managing and securing access to critical resources. The capabilities of IAM extend beyond simple access controls, offering sophisticated tools that tailor access based on a variety of conditions and ensuring compliance through detailed reporting.
Key Benefits of IAM Capabilities:
- Granular Access Control: IAM systems allow organizations to fine-tune access permissions with exceptional granularity. For instance, permissions can be adjusted based on the time of day, user location, and specific user attributes, providing a highly customizable approach to access management.
- Platform Access Restrictions: IAM is crucial in regulating access to critical development environments. Organizations can limit access to platforms involved in the development, staging, and testing phases, thereby protecting these sensitive areas from unauthorized access and potential threats.
- Data Transmission Security: IAM enhances data security by setting strict permissions on who can create, modify, or delete sensitive data. It controls how data is transmitted within and outside the organization, preventing unauthorized data leaks. For example, role-based access control (RBAC) can be used to ensure that temporary employees do not send or receive data beyond the company’s secured systems.
- Reporting and insights: IAM systems generate detailed reports that not only help organizations demonstrate compliance with data security and privacy regulations but also provide valuable insights. These insights assist in refining security strategies, reducing risk, and understanding the resource needs of employees to boost productivity.
Understanding and implementing the right Identity and Access Management (IAM) capabilities is crucial for safeguarding your organization's digital assets and ensuring efficient operation. Tools like PAM, MFA, and SSO are more than just security measures; they empower your teams with streamlined access, reduce IT overhead, and ensure compliance with stringent regulations. These IAM solutions protect sensitive information and secure your infrastructure against evolving threats by addressing identity lifecycle processes and access rights management.
At miniOrange, we specialize in delivering these essential IAM solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of your business. Our expertise ensures that your security architecture not only protects but also enhances your operational capabilities. Choose miniOrange to fortify your digital landscape and experience a secure, compliant, and efficient environment. Secure your future with miniOrange—where security meets simplicity.
Author



Leave a Comment