Introduction to iOS MDM Profile
Managing a fleet of iOS devices without proper control can be a nightmare for businesses. Imagine your business experiencing unauthorized data access, lost devices, and security vulnerabilities—all leading to financial losses and reputational damage. An iOS Mobile Device Management (MDM) profile can help alleviate this by providing a centralized way to enforce security policies, configure settings, and manage applications without needing physical access to devices.
Businesses and IT administrators can remotely create and deploy MDM profiles, ensuring company-owned and employee devices adhere to strict security policies. This prevents unauthorized access, reduces the risk of data breaches, and ensures seamless device management.
Why Use MDM Profile on the iOS Devices?
A Mobile Device Management (MDM) profile is crucial for organizations to manage iOS devices securely without manual setup. Key benefits include:
1. Centralized Management: IT admins can control multiple devices from a single dashboard, reducing manual workload and ensuring consistency.
2. Enhanced Security: Enforce strict security protocols like passcode policies, encryption, and remote wipe capabilities to prevent data breaches.
3. Compliance Assurance: Ensure adherence to company policies and industry regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. Remote Access & Support: IT teams can troubleshoot, update, and monitor devices remotely, minimizing downtime and enhancing efficiency.
4. Scalability & Flexibility: Whether managing a few devices or thousands, MDM profiles support scalable deployments in enterprises, schools, and government agencies.
5. Wider Application: Enterprises, schools, and government agencies use MDM for security, content filtering, and application management.
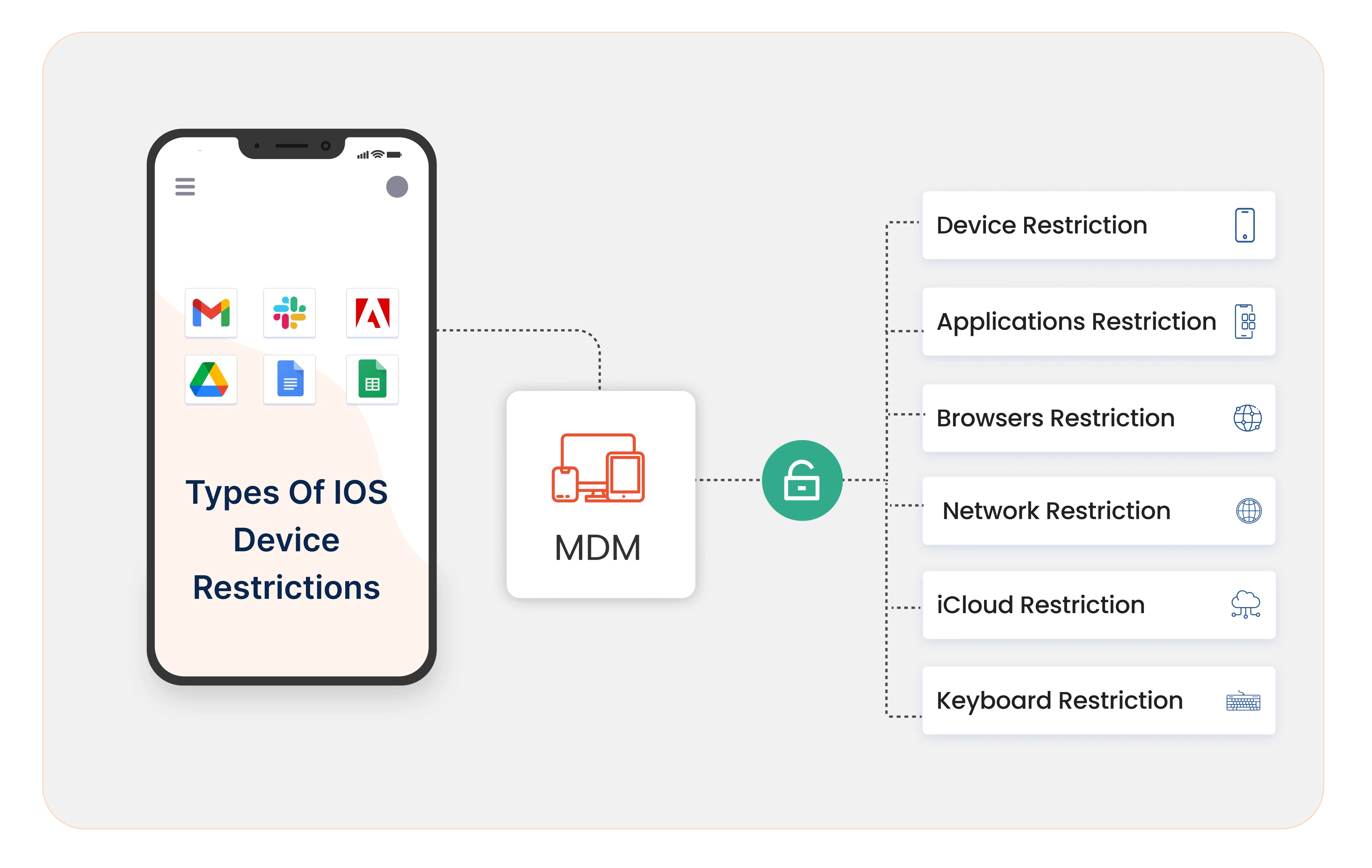
Key Features of iOS MDM
An iOS Mobile Device Management (MDM) Profile enables organizations to remotely manage and secure their Apple devices, such as iPhones and iPads. Key features included.
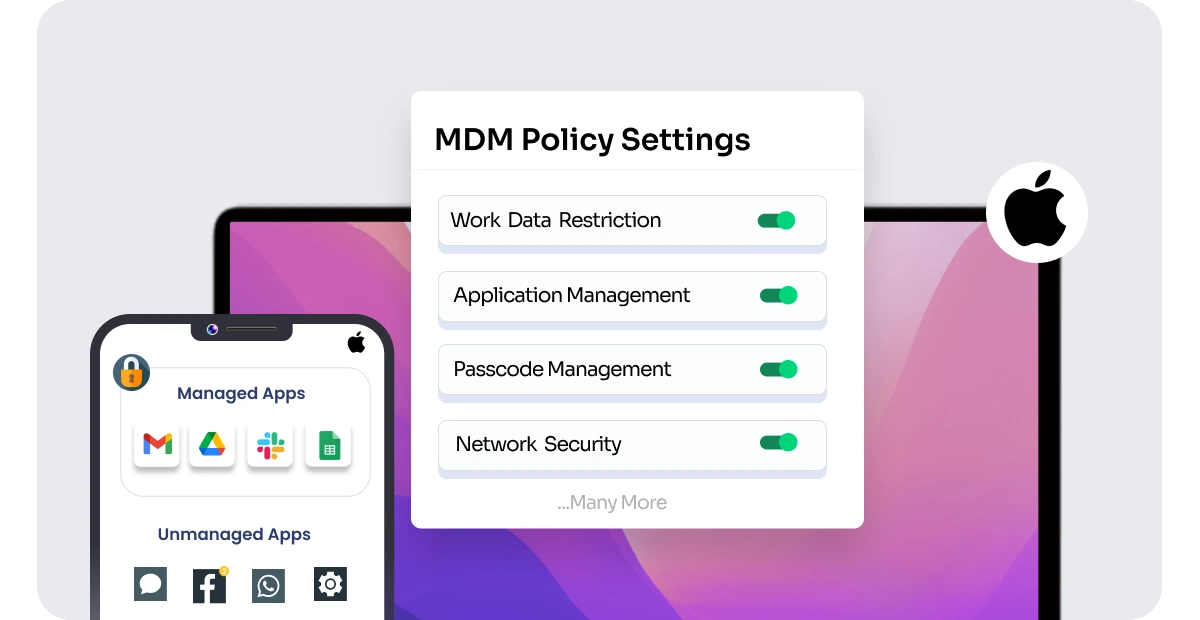
1. Work data settings
A. Sharing Data Between Managed and Unmanaged Apps
Allow or restrict copy and paste actions done from managed to unmanaged apps. With this setting, you can restrict the sharing of work data and copy-paste between managed and unmanaged applications.
B. Managed Apps to edit info of unmanaged accounts
Allow or restrict managed apps to add/edit contact information to unmanaged contact accounts. This setting will be forced enabled if ‘Share data between managed and unmanaged apps’ is allowed.
C. Unmanaged Apps to edit contacts of work-managed accounts
Enable or disable unmanaged applications to add/edit contacts to work-managed accounts. This setting will be forced if Share data between managed and unmanaged apps is enabled.
D. AirDrop as unmanaged drop point
Configure if work documents and files from managed applications can be shared via AirDrop. This setting will be forced enabled if you enable the ‘Airdrop as unmanaged drop point’ setting.
E. Camera and Screenshot Setting
Allow/Restrict employees from using cameras and FaceTime and taking screenshots on supervised iOS devices. In the case of BYOD devices, these settings are applied at a device level and not at the managed applications level.
F. Force Encrypted Backups
Allow or restrict users to enforce encrypted backups, where they can set a password for encrypted files while taking backup.
2. Passcode Policy
miniOrange MDM provides a device-level passcode policy for both BYOD and company-owned devices. It offers two types of passcode settings:
A. Basic Settings
- Passcode Type: Choose between numeric or alphanumeric passcodes.
- Minimum Passcode Length: Set a minimum length for passcodes up to a minimum of 16 characters.
B. Advanced Settings
- Enforce Complex Passcode: Specify the minimum number of symbols that employees must include in their passcodes to enhance security.
C. Passcode Management Settings
- Passcode Expiry Period: Define how often employees must update their passcodes to maintain security, ranging from immediately to 2 years.
- Passcode History List: Limit the reuse of old passcodes by specifying the number of previous passcodes that cannot be reused.
- Maximum Failed Attempts: Set a limit on the number of failed passcode attempts before the device performs a factory reset in case of iOS and device lock in case of macOS, protecting against unauthorized access.
- Maximum Inactivity Time: Specify the maximum period of inactivity before the device automatically locks, ensuring it is not left vulnerable when unattended.
- Maximum Grace Period for Device Lock: Define a grace period during which the device can be unlocked without re-entering the passcode, providing convenience while maintaining security.
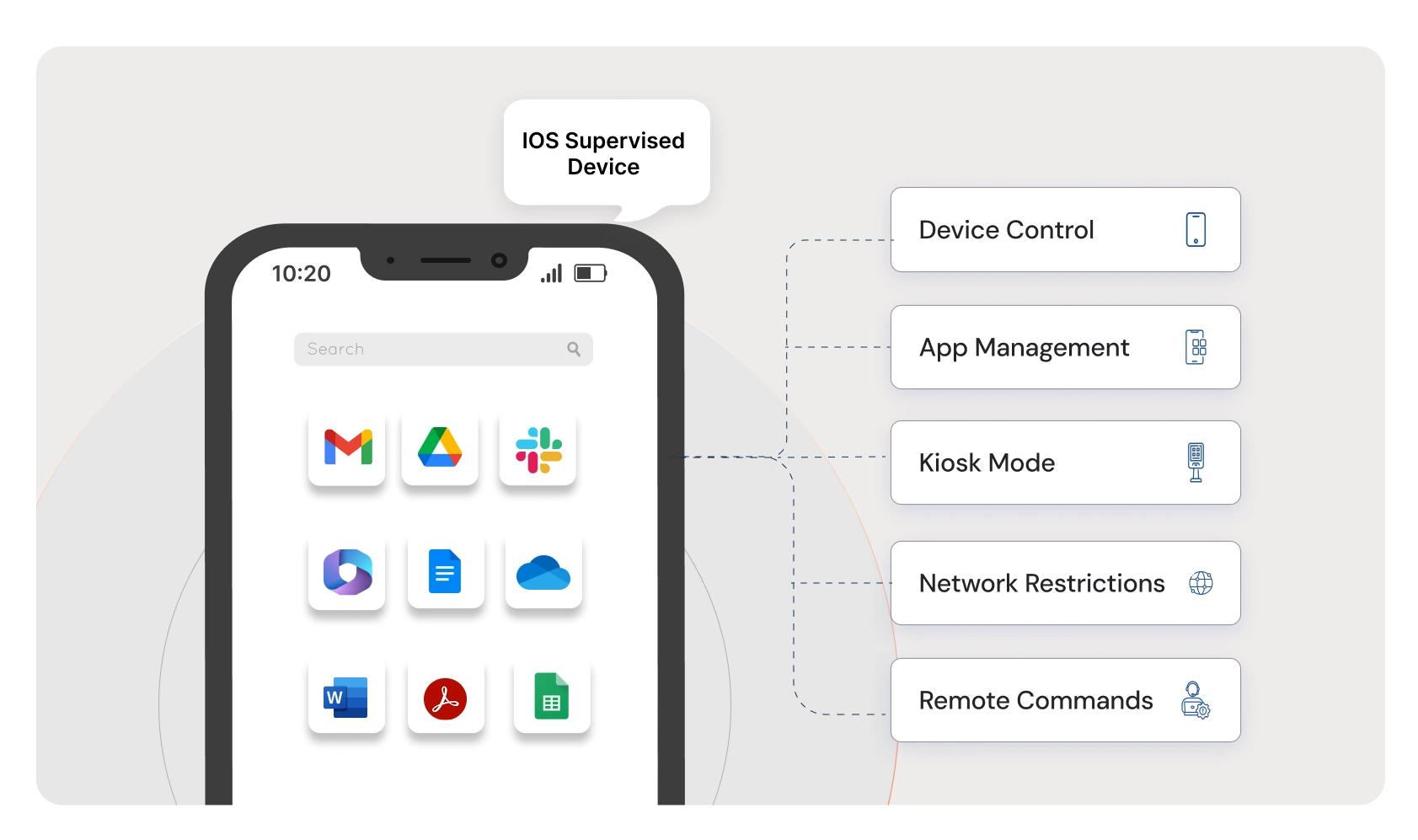
3. Application Management
Control the set of applications that the users have access to on the iOS devices. Allow or block a set of applications and control app visibility on supervised iOS devices. In the case of unsupervised/BYOD devices, enterprises can only publish the required application on employee devices. IT admin cannot block an application on a BYOD device.
Applications installed via an MDM are called managed applications. Admin can also prevent data sharing between the managed and the unmanaged apps.
A. Single App Mode (Kiosk Mode):
Single-app mode (SAM) or Kiosk mode enables enterprises to set one application to run continuously, making it ideal for supervised iOS devices used in kiosk setups. This is particularly helpful in banking, schools, or any organization where employees do the field work and use only a single app on the phone as a part of their job.
B. Convert apps:
Convert unmanaged apps (apps that are already installed by the user on a BYOD iOS device) into managed apps. If the device is supervised, the switch to a Managed app from an unmanaged app happens without user interaction if requested by the MDM solution. If the device isn’t supervised, the user must formally accept management. App conversion isn’t supported with the account-driven user enrollment into MDM.
C. Configurations Settings for Managed Applications
miniOrange provides the admin with the ability to configure settings for all managed applications. For example, in the case of Microsoft Outlook or Gmail, the admin can configure which email addresses can be logged into the application. In the case of Slack, the admin can preconfigure which workspace can be accessed in the application.
D. Device App Settings
Configure permissions for various applications, including iMessage, iTunes, News, Podcasts, Music Services, Radio Services, Bookstore and AirDrop. Additionally, allow or restrict users from deleting System applications on supervised iOS devices.
4. Network Settings
- Wifi configuration: Push a pre-approved list of Wi-Fi connections to limit access to certain networks. This ultimately restricts users from connecting to unreliable or public Wi-Fi.
- VPN configuration: Push a pre-approved VPN at device level or at per-app level so that the work data flows through a secure network.
- Bluetooth configuration: Enable or disable Bluetooth and Hotspot on iOS devices. This is possible only on supervised devices.
- Airdrop configuration: Enable or disable Airdrop on iOS devices, and also make Airdrop an unmanaged location so that data from managed applications doesn't get shared via Airdrop.
5. Safari Settings
Choose to allow or restrict Safari on the supervised iOS device or not. Also, control to allow or deny autofill, popups, javascript, cookies, and fraud warning settings.
6. Siri & iCloud Settings
In unsupervised devices, the following settings can be controlled by the IT admin.
Siri: Allow or restrict end users from using Siri on their iOS devices.
iCloud Document Sync: Allow or restrict users from syncing data and documents from managed apps.
In supervised devices, the IT admin can allow or restrict users from doing device backup, keychain sync, photo library sync, iCloud private relay, etc.
Setting Up miniOrange iOS MDM Profile
Here are the steps to Enroll in iOS MDM solution:
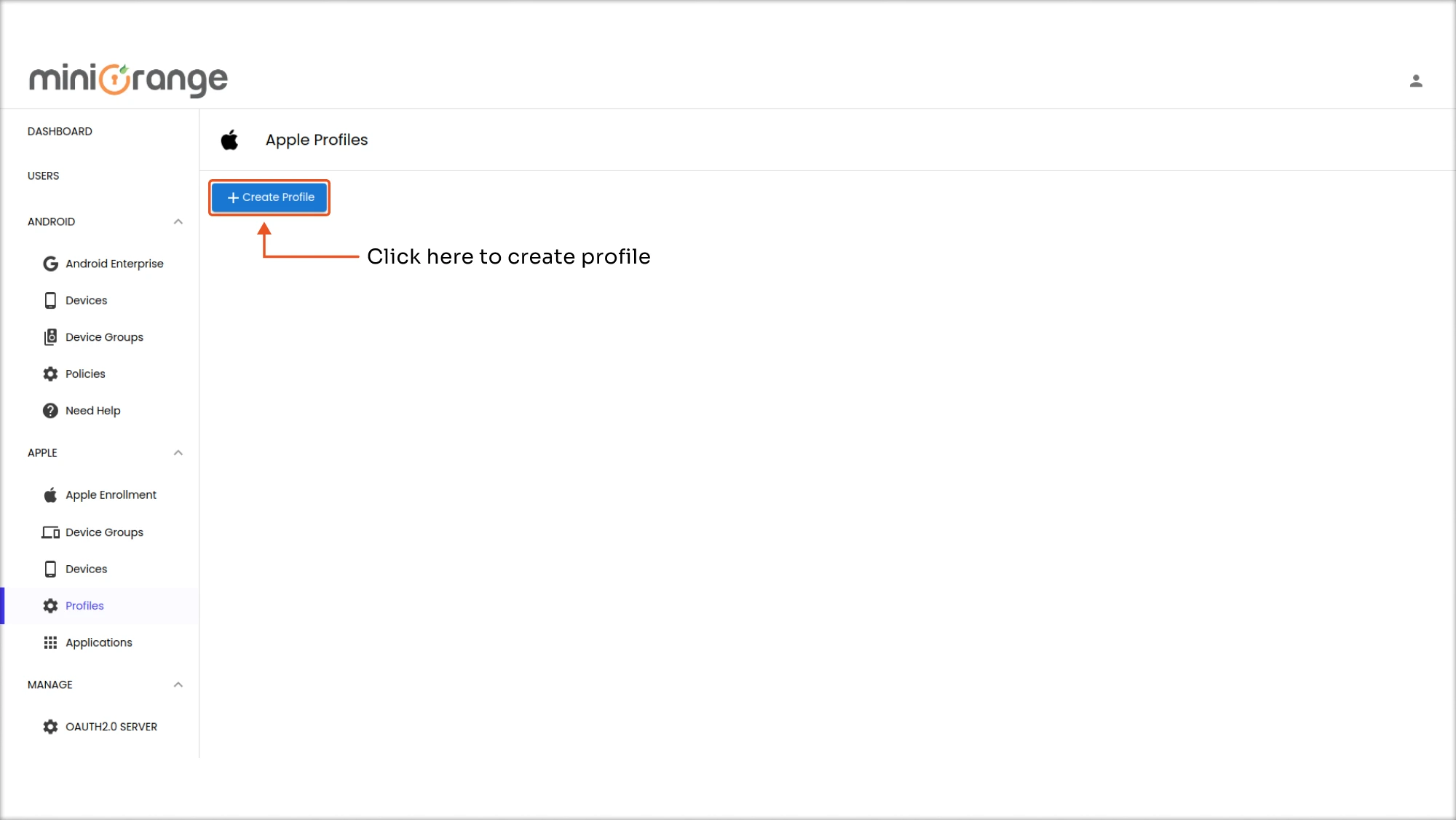
Step 1: Access the MDM Dashboard
- Log in to your miniOrange MDM dashboard.
- Navigate to APPLE > Profile.
- Click Create Profile to start the setup.
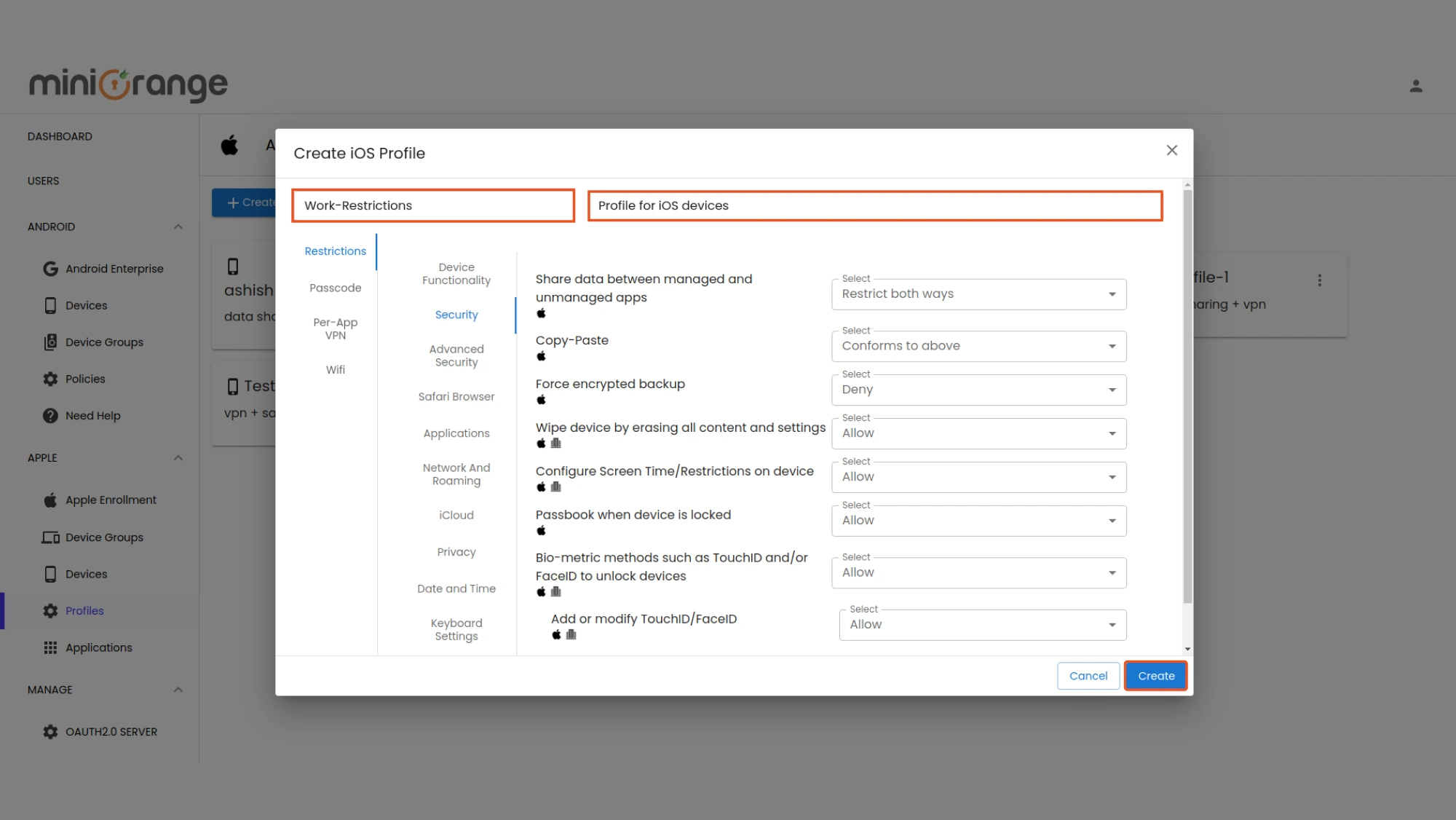
Step 2. Configure Device Restrictions
- Set name and description for policy, Wi-Fi configurations, and VPN settings.
- Define security policies such as AirDrop restrictions, App blocklists, camera usage control, and more.
- After adding the restrictions, click on the create button to create a profile.
Step 3: Save and Deploy
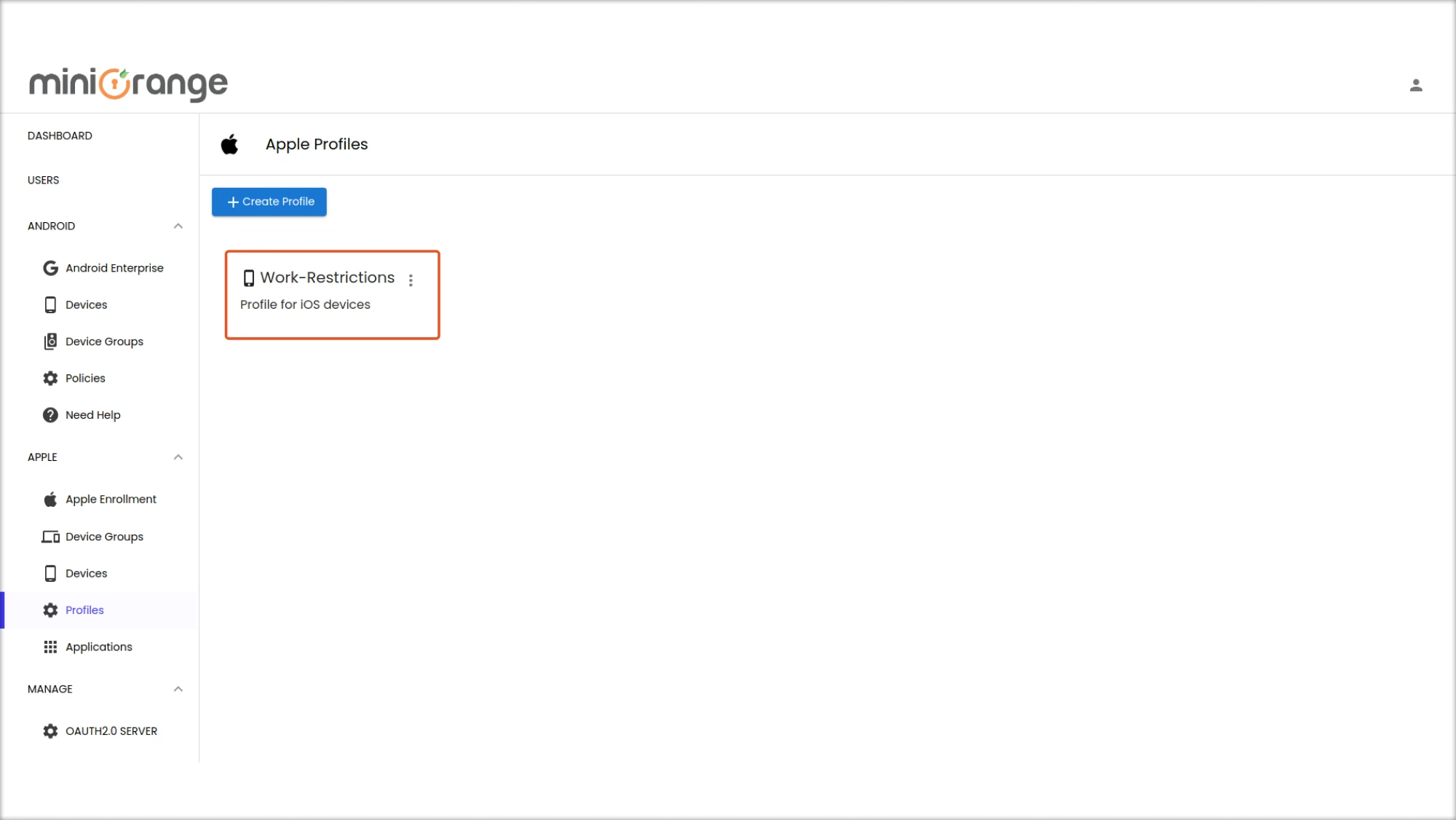
- Once all configurations are set, deploy the profile to all required iOS devices remotely.
- Monitor and manage compliance through the miniOrange MDM dashboard.
Benefits for Enterprises and IT Admins
An iOS MDM profile provides businesses with a set of essential features that streamline Apple device management while enhancing security. Some key features include:
1. Security Management
A strong security posture is crucial to protecting business data. The iOS MDM solution from miniOrange provides comprehensive security features:
- A. Remote Wipe: If a device is lost or stolen, IT teams can remotely wipe sensitive data to prevent unauthorized access.
- B.Enforce Strong Passcode Policies: Enforce minimum passcode length, complexity requirements, and auto-lock settings to prevent unauthorized access.
- C. App Restrictions: Control app installation by restricting access to non-approved applications that may pose security threats.
- D. Jailbreak Detection: Prevent jailbroken devices from accessing corporate resources and enforce security compliance.
- E. Data Encryption: Ensure that sensitive corporate data is encrypted both at rest and in transit.
2. Device Configuration
Proper device configuration enhances usability and security while reducing IT workload. Our iOS MDM enables IT admins to:
- A. Wi-Fi & VPN Configuration: Automatically configure and enforce Wi-Fi and VPN settings for secure connectivity.
- B. Email & Account Setup: Seamlessly deploy and configure corporate email accounts on all enrolled devices.
- C. App Deployment & Management: Ensure employees have access to necessary business applications by pre-installing or restricting certain apps.
- D. Automatic Software Updates: Keep devices secure and optimized by remotely managing system updates and security patches.
- E. Bluetooth & Hotspot Controls: Restrict or allow Bluetooth, hotspot, and tethering features to maintain security and manage data usage.
3.Compliance Enforcement & IT Management
For organizations that must adhere to industry regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, or SOC 2, iOS MDM ensures compliance through:
- A. Automated Policy Enforcement: Apply organization-wide security settings to maintain compliance without manual interventions.
- B. Real-Time Monitoring & Reporting: IT teams can monitor device usage, location, and application activity.
- C. Audit Logs & Reports: Keep track of compliance history and detect policy violations before they cause significant harm.
- D. Geofencing & Location Tracking: Get real-time location data to track lost or stolen devices and enforce location-based policies.
- E. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign different levels of access to employees based on their job roles to prevent unauthorized data access.
Conclusion
With the rapid adoption of iOS devices in workplaces and educational institutions, having a robust iOS MDM profile is no longer optional—it's a necessity. The cost of inadequate device management is too high, leading to security breaches, regulatory penalties, and operational inefficiencies.
By implementing an iOS MDM solution like miniOrange, enterprises can centralize device management, strengthen security protocols, streamline device configuration, and ensure compliance with industry standards. Investing in a comprehensive MDM solution not only protects your business but also enhances productivity and IT efficiency. Don’t wait until a security breach happens—take control of your Apple devices today!
Additional Resources
Author

Leave a Comment