In today's digital landscape, cloud computing has become the backbone of modern enterprises, enabling scalability, flexibility, and efficiency. However, as organizations embrace this transformative technology, the need for robust security frameworks has never been greater. With sensitive data and critical resources increasingly hosted in cloud environments, businesses face heightened risks of cyberattacks targeting privileged accounts.
This is where Cloud Privileged Access Management (PAM) steps in. Designed to safeguard elevated access to critical cloud resources, privileged access management in the cloud ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information. As businesses transition from legacy systems to modern architectures, implementing a cloud PAM solution becomes essential to bridge the gap between on-premises systems and privileged access management for the cloud.
By leveraging enterprise cloud PAM, organizations can secure their environments while maintaining seamless access for legitimate users. This blog explores the challenges of implementing privileged access management cloud solutions and highlights the transformative benefits of cloud-based privileged access management in mitigating security risks and strengthening enterprise defenses.
What is Cloud Privileged Access Management?
Cloud Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a security framework specifically designed to protect critical data and resources in cloud environments. It focuses on managing, controlling, and monitoring access to privileged accounts—those with elevated permissions capable of accessing sensitive information or performing critical functions. By ensuring that only authorized individuals can use these accounts, cloud-based privileged access management mitigates the risks of unauthorized access, accidental data exposure, or malicious actions.
This framework is important for securing modern enterprises as it provides robust controls to handle complex challenges unique to cloud environments. With features like activity monitoring, role-based access, and real-time alerts, privileged access management for the cloud enhances overall security, ensuring that businesses can leverage the cloud safely and efficiently.
What Are the Key Terms in Cloud PAM?
Understanding Cloud Privileged Access Management (PAM) requires familiarity with essential terms that form the foundation of cloud and multi-cloud security. These concepts highlight the technologies and strategies crucial for effectively managing privileged access in cloud environments.
1. Privileged Access
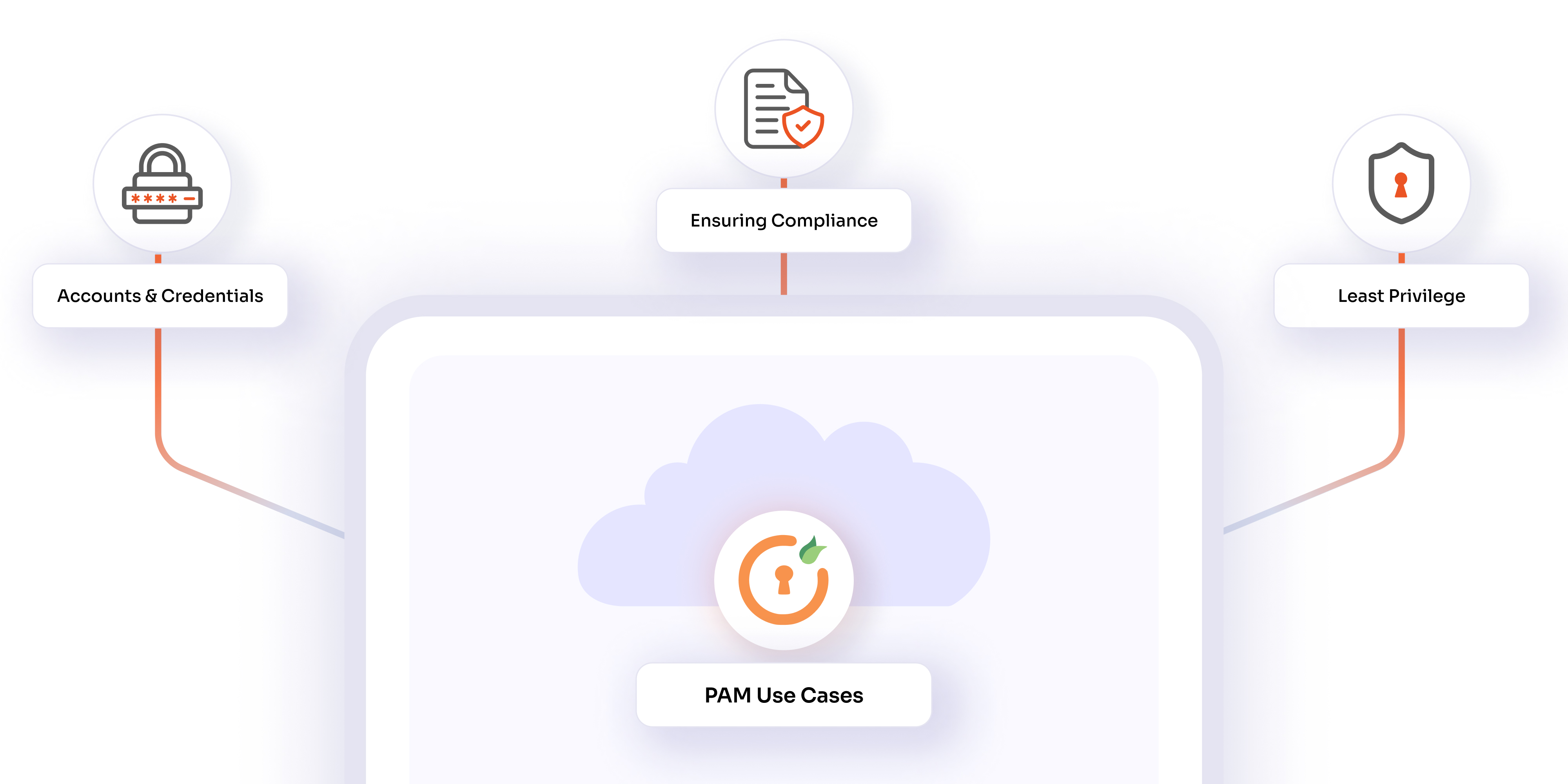
Privileged access refers to the elevated permissions granted to users or systems that enable them to access sensitive data, configure systems, or manage critical applications. In the context of privileged access management for the cloud, controlling and monitoring these elevated permissions is essential to preventing unauthorized access and reducing security risks.
2. Zero Trust
The Zero Trust security model operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It requires strict identity verification for every user or device attempting to access resources, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network. In cloud-based privileged access management, Zero Trust ensures that no complete trust is given to privileged accounts, strengthening overall cloud security.
3. Just-In-Time Access (JIT)
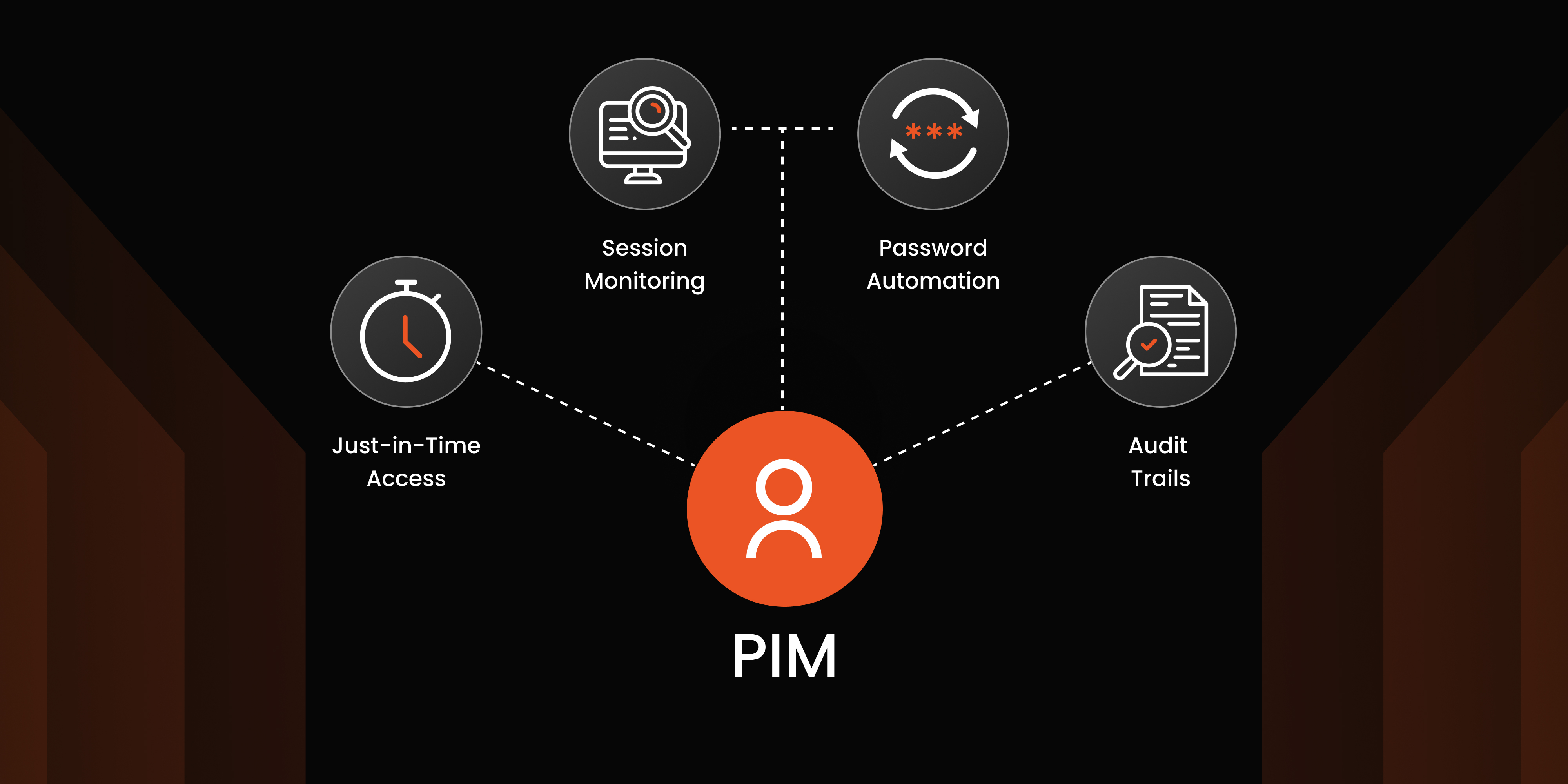
JIT access is a security strategy that provides users with privileged permissions only for the duration required to complete a specific task. This temporary access minimizes the risks associated with standing privileges and reduces the attack surface in privileged access management cloud systems.
4. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
SaaS refers to third-party software delivered over the internet, offering scalability, flexibility, and ease of management. In cloud PAM solutions, SaaS components enable secure deployment and centralized management of credentials, simplifying operations for businesses.
5. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides cloud-based infrastructure like virtual machines, storage, and servers. In privileged access management in the cloud, IaaS platforms offer scalable environments to store and manage credentials while ensuring robust security for cloud operations.
6. PAM-as-a-Service (PAMaaS)
PAMaaS is a cloud-based delivery model for deploying privileged access management for the cloud. By leveraging hybrid or multi-cloud environments, PAMaaS solutions combine the benefits of SaaS and IaaS to provide a seamless transition from legacy systems to enterprise cloud PAM frameworks.
Why PAM Is Critical for the Cloud
The cloud has revolutionized how businesses operate, but it also introduces unique challenges in managing privileged access. Without robust security measures like Cloud Privileged Access Management (PAM), organizations risk exposing sensitive data and critical systems to a range of threats, including insider misuse, unauthorized access, and devastating breaches.
Challenges in Managing Privileged Access in the Cloud
- Complex Security Models: Traditional PAM solutions designed for on-premises environments often struggle in the cloud, where dynamic and distributed systems demand continuous monitoring and the ability to trace interactions across multiple cloud services.
- Shared Accounts: Cloud environments often rely on shared accounts across multiple employees, making it difficult to track individual user activities and enforce granular access controls.
- Standing Privileges: Admins may be tempted to configure standing privileges, granting indefinite access to users. While convenient, this opens the door for misuse, as users may access resources they no longer need.
- Multi-Service Configurations: Configuring PAM for diverse cloud services, like virtual machines, containers, and storage, adds complexity and requires significant time and effort.
- Administrative Strain: Manual tasks such as user onboarding, credential rotation, and privilege management can overwhelm IT teams, leading to inefficiencies and potential security gaps.
Risks of Not Implementing PAM in the Cloud
Failing to adopt privileged access management for the cloud significantly heightens the risk of:
- Insider Threats: Without strict controls, privileged users can intentionally or unintentionally misuse their access to compromise sensitive data.
- Security Breaches: Standing privileges, misconfigured permissions, and shared accounts make it easier for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Data Leakage: The lack of visibility and monitoring across cloud services increases the chances of sensitive information being accessed or exposed.
The Difference Between PAM in the Cloud and PAM for the Cloud
When exploring privileged access management cloud solutions, it’s important to distinguish between PAM in the cloud and PAM for the cloud. While both address privileged access security, their implementation and focus vary significantly.
PAM in the Cloud
PAM in the cloud refers to replacing traditional on-premises PAM systems with fully cloud-based architecture. It is typically a component of PAM-as-a-Service (PAMaaS), where third-party providers manage and deliver the PAM solution using a cloud-based privileged access management approach. This method leverages hybrid or multi-cloud environments, enabling organizations to access the latest security technologies without the burden of managing on-premise infrastructure.
Key Features of PAM in the Cloud:
- Centralized management of privileged access across cloud and hybrid environments.
- Scalability and flexibility, allow businesses to adapt to changing demands.
- Seamless integration with modern cloud-native applications and services.
PAM for the Cloud
On the other hand, PAM for the cloud focuses on securing access to cloud-based applications and services, regardless of whether the PAM solution itself is hosted in the cloud or on-premises. Organizations often use legacy PAM systems in this context, which can pose challenges when securing cloud environments. For example, older systems may lack the ability to address specific threats like machine-to-machine (M2M) attacks in cloud ecosystems.
Key Features of PAM for the Cloud:
- Enables access control for cloud applications, even with legacy PAM systems.
- May lack advanced features like continuous monitoring and Zero Trust architecture if not optimized for cloud environments.
- Often requires additional configurations to secure cloud data effectively.
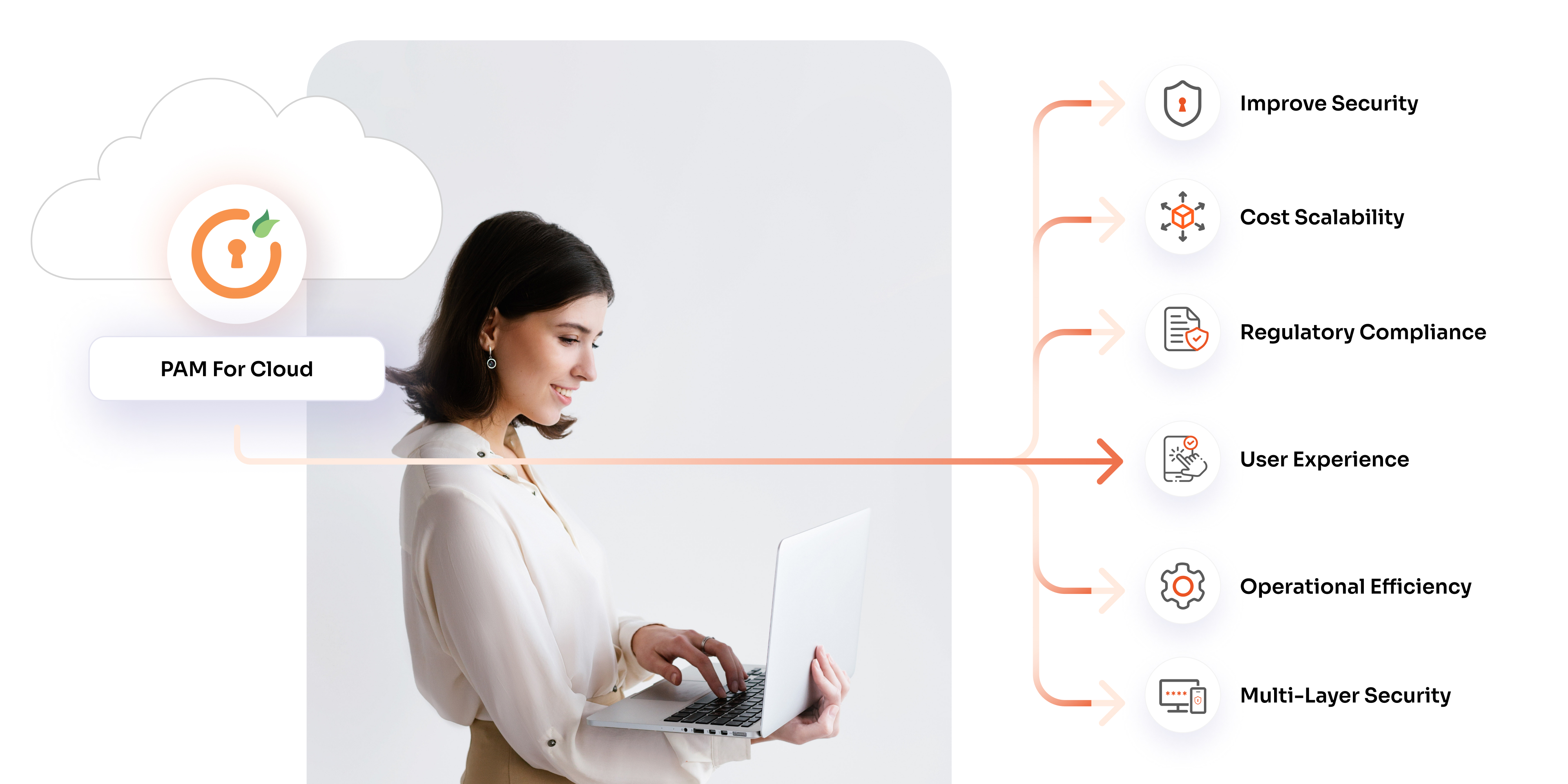
Benefits of PAM in the Cloud
Privileged Access Management (PAM) in the Cloud is revolutionizing how organizations secure sensitive resources and manage elevated permissions. Unlike traditional on-premises systems, cloud-based privileged access management delivers unparalleled scalability, efficiency, and advanced security. Here’s how it benefits modern enterprises:
1. Enhanced Security for Multi-Cloud Environments
Managing privileged access across multiple cloud platforms can be challenging. Privileged access management in the cloud centralizes control, providing stronger defense mechanisms against unauthorized access and M2M (machine-to-machine) attacks. It offers real-time monitoring, secure access tiers, and automated password rotations, ensuring consistent security across diverse cloud ecosystems.
2. Cost-Effective Scalability
With PAM-as-a-Service (PAMaaS), organizations eliminate the need for costly hardware investments and reduce maintenance overhead. The ability to scale up or down based on business needs ensures that companies only pay for what they use, making privileged access management for the cloud a highly flexible and budget-friendly solution.
3. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Maintaining compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and other industry-specific standards is a critical priority for enterprises. Cloud-based privileged access management incorporates built-in features and tools to ensure organizations meet stringent data security and privacy requirements, reducing the risk of costly penalties or breaches.
4. Streamlined User Experience
Privileged access management cloud solutions simplify the user experience by automating repetitive tasks such as password rotations and access assignments. Administrators benefit from a unified interface, making it easier to manage multi-cloud environments efficiently. Users, on the other hand, enjoy secure, seamless access without unnecessary delays or friction.
5. Operational Efficiency through Automation
Manual management of credentials and privileges can be error-prone and resource-intensive. Enterprise cloud PAM automates tasks like onboarding, offboarding, and access monitoring, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic priorities rather than day-to-day operational demands.
6. Robust Multi-Layer Security
With advanced features like Zero Trust architecture, role-based access, and secure authentication processes, cloud PAM solutions deliver a multi-layered security framework. This reduces vulnerabilities associated with standing privileges and ensures sensitive data remains protected across all cloud services.
What Are the Common Challenges with Cloud PAM?
Migrating Privileged Access Management (PAM) to the cloud is essential for modern enterprises, but it comes with its own set of challenges. Addressing these issues is critical to ensuring that cloud-based privileged access management solutions deliver robust security and seamless functionality.
1. Securing Credentials During Migration
Moving privileged access systems to the cloud introduces risks to passwords and access credentials. Without proper safeguards, these sensitive elements can become vulnerable during the transition. It’s crucial to ensure that credentials are encrypted both in transit and at rest, incorporating encryption key management (EKM) to add an extra layer of protection against potential breaches.
2. Outdated Security Policies
Many businesses face the challenge of adapting legacy security policies to fit cloud environments. Policies designed for on-premises setups often fail to address the complexities of remote access and distributed teams. This disconnect can leave cloud environments exposed to unauthorized access and insider threats. Updating security policies to align with cloud-specific requirements is essential for a secure privileged access management cloud implementation.
3. Adjusting to Cloud-Specific Access Needs
Unlike traditional setups, cloud environments often require multi-layered access credentials. For example, organizations may need to implement two-factor authentication that includes device-level and application-level verifications. Without these adjustments, cloud PAM solutions risk falling short in preventing unauthorized access.
4. Lack of Visibility Across Multi-Cloud Environments
Managing privileged access across multiple cloud platforms can lead to a fragmented security landscape. A lack of centralized visibility makes it difficult for admins to monitor access, enforce policies, and respond to threats in real-time.
5. Administrative Complexity
Cloud migration often increases the workload for administrators, particularly when dealing with encryption, password rotation, and access management for a wide range of services. Without proper automation and streamlined processes, this can lead to inefficiencies and human error.
6. Resistance to Change
Adopting privileged access management for the cloud requires rethinking established practices and retraining teams. Resistance to change, coupled with a lack of expertise in cloud-specific PAM implementations, can slow down adoption and leave gaps in security.
Cloud Security Best Practices
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud environments, maintaining robust security while ensuring operational efficiency is paramount. To achieve this balance, adopting effective Privileged Access Management (PAM) practices is essential. Below are some key best practices for securing your cloud infrastructure.
1. Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
The foundation of a secure cloud PAM strategy lies in adhering to the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP). This principle ensures that users are granted access only to the resources and information necessary for their role, minimizing the risk of accidental or intentional misuse. By limiting privileges, organizations reduce their attack surface and protect critical assets from unauthorized access.
For instance, implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) access can dynamically provision access rights, ensuring users only have permissions for the time and tasks required, thus aligning with Zero Trust principles.
2. Regularly Audit and Monitor Privileged Sessions
Monitoring and auditing privileged sessions is critical for identifying potential security threats in real-time. By maintaining a comprehensive record of all privileged activities, organizations can:
- Detect unusual or suspicious behavior.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Conduct thorough investigations in case of security incidents.
Automated PAM tools equipped with advanced session monitoring capabilities can provide actionable insights. They dynamically adjust access permissions based on real-time risk assessments, enhancing both security and efficiency.
3. Integrate PAM with Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Integrating PAM with your Identity and Access Management (IAM) system creates a unified framework for managing user authentication and authorization. This integration ensures:
- Seamless management of user identities across cloud and on-premises environments.
- Enhanced visibility into access patterns and potential risks.
- Improved scalability for hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures.
Additionally, combining PAM with data encryption and enterprise key management (EKM) solutions strengthens your security posture. A unified approach to encryption key management and privileged access ensures that sensitive data remains protected while facilitating secure, efficient workflows.
Next Step! Secure Your Cloud with miniOrange PAM Solution
Securing privileged access in the cloud is essential. miniOrange PAM Solution simplifies cloud security with features like Just-In-Time (JIT) access, Zero Trust architecture, session monitoring, and seamless IAM integration. Designed for multi-cloud and legacy transitions, it enhances security, compliance, and efficiency through automation and centralized management.
Protect your cloud resources with miniOrange PAM—secure, scalable, and seamless!
Author





Leave a Comment