How to secure ASP.NET with your Ethereum account
A common problem that arises when using Decentralized Applications (dApps), or other services that function on a blockchain, is being able to quickly and securely authenticate a user so they can log in with ease.
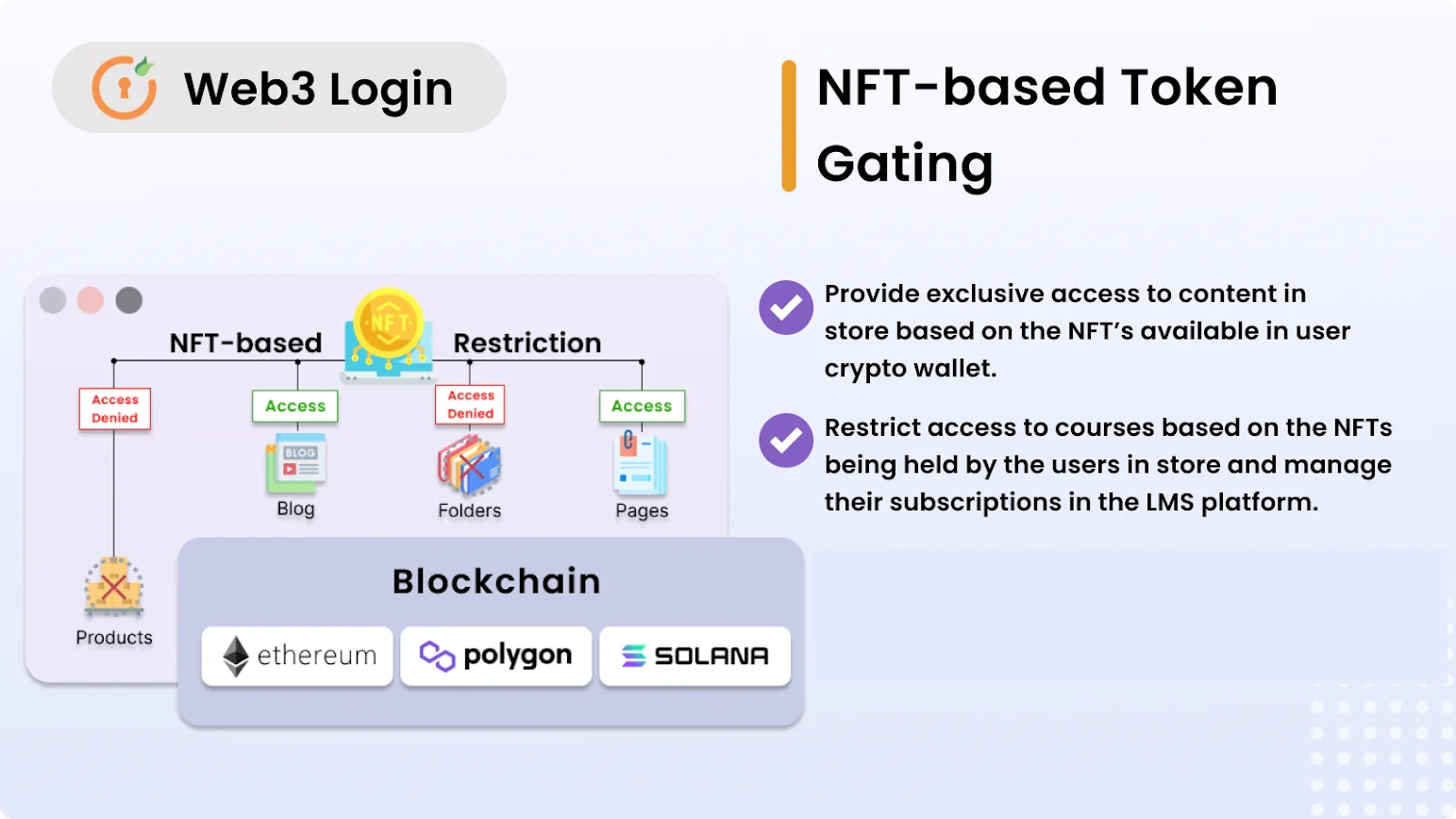
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into all things web3 and explore how you can access blockchain-based services using your cryptocurrency account as an authentication tool. The main component necessary to accomplish this is an API layer that serves to exchange the user’s credentials. Let’s take a look at how we can do that.
What is a blockchain?
In simple terms, a blockchain is a digital ledger that contains records of transactions in ‘blocks’. Unlike traditional ledgers that are stored and maintained in one location by a centralized administrator, this ledger is decentralized and distributed across multiple computers.
The advantage of using such a blockchain compared to centralized systems is primarily the ability to verify and audit transactions independently, at a low cost, and with a high degree of fidelity. This is mainly because any independent record or block cannot be accidentally or maliciously altered without altering all subsequent ‘blocks in the chain’.
What is a cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a digital commodity, security, or currency that is designed to work on a distributed, decentralized network rather than a central authority like a bank or government. In this case, it refers to a blockchain that operates on a peer-to-peer network.
The name cryptocurrency comes from the fact that it is secured using cryptographic algorithms. Since the currency is on a distributed ledger, where every person has access to a record of every transaction, encrypting the data is a necessity.
Types of cryptocurrencies in the market
- Bitcoin: The first, most well-known, and most widely used cryptocurrency is Bitcoin. It also has the highest market capitalization of all cryptocurrencies by far, crossing over $800 billion in 2022. Various examples of decentralized digital currencies emerged following its creation. However, Bitcoin stayed at the forefront, growing significantly in popularity in 2017 and exploding in 2022.
- Ethereum: The second most popular and second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization is Ethereum. Released in 2015, it stood out among over a thousand other cryptocurrencies due to its unique feature of smart contracts. We’ll talk more about Ethereum in detail in the next section
- Tether: Tether is unique in that its value is fixed to that of the US Dollar. Such a cryptocurrency is called a stablecoin. This may attract some traders who are concerned with the volatile nature of other currencies that tend to rise and fall substantially over a short period. However, Tether’s main function is that of a medium when traders wish to move from one cryptocurrency to another.
- Binance Coin: Binance is the 3rd largest cryptocurrency by the price of an individual coin and the 4th largest overall by market capitalization. It is issued and managed by Binance, the largest cryptocurrency trading exchange in the world. Although it can be used for purchasing a variety of goods and services, it has been banned in some countries.
- USDC: USD Coin is another example of a stablecoin whose value is fixed to that of the US Dollar. However, unlike Tether, it is claimed to be fully backed by dollars held in reserve, which are also regulated by US institutions. This makes it seem safer and more reliable than its alternatives.
Ethereum
We talked a bit about Ethereum above, but let’s look at everything this cryptocurrency offers. Ethereum was conceived in 2013 and released in 2015. This is relatively late, compared to other early currencies like Bitcoin. However, it has still achieved massive success in a short time, owing to its unique ability to offer a wide range of functions across a variety of applications.
Cryptocurrency: To make it easier to distinguish between the technology and the actual currency itself, the former is called Ethereum while the latter is called ether. Therefore, ether can be used to pay for goods and services, provided it is accepted in that particular market. To do so, you require a digital wallet, which generally represents the address to which your money is tied.
Smart contracts: A smart contract is generally just a program that automatically runs when a contract’s conditions are met. They can also be classified as a type of Ethereum account, ones that have a balance and can send transactions over the network. However, they are not individually controlled. Rather they strictly adhere to the code and run as programmed.
Decentralized applications: Unlike regular mobile apps that function on centralized servers that belong to and are operated by particular companies, decentralized applications (dApp) run on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network that is based on a blockchain. Ethereum powers these apps to perform tasks, much like a regular app, such as playing games, investing, performing transactions, or making use of certain services that you regularly would.
NFTs: Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are unique, and therefore non-interchangeable, tokens or units of data that are tied to and represent certain digital assets. These tokens are stored on a digital ledger using blockchain technology, the same as Ethereum or other cryptocurrencies. Therefore, NFTs can increase or decrease in value and can be traded on the market. The value of NFTs is directly tied to the perceived value of the audio, video, or image files that they represent.
DeFi: Decentralized Finance (DeFi) comprises a variety of financial applications and instruments that compete with legacy digital payment methods. It is aimed at removing middlemen and financial intermediaries that are commonplace in centralized systems. DeFi also makes use of smart contracts. This is the reason most decentralized finance applications are built on top of Ethereum.
Benefits of Web3 authentication to ASP.NET
Now, let’s consider a situation where you want to use your Ethereum account as user credentials to log into a decentralized ASP.NET app. The idea is to issue a JWT token in exchange for the user’s credentials.
However, instead of forcing the user to make a transaction, we could instead require them to sign a text message using their private key. Web3 authentication allows you to do this. Take note that, for this to work, you need to be signed in to your account.
The benefits of this method are:
- No transaction required: Using web3 authentication means the user won’t have to make a transaction every time they want to log in to the ASP.NET app. Therefore, this saves them resources that would otherwise be wasted just for performing a simple authentication process.
- Faster authentication: The user doesn’t have to wait long for the authentication process to complete. All they have to do is click a single button while logged into their Ethereum account.
- Privacy: If users are forced to perform a transaction to log into their ASP.NET dApps, their login operations become permanently public and part of the Ethereum blockchain. This is not the case with Web3 logins, which also indirectly reduces the overall size of the cryptocurrency.
- Simple-to-use: Another benefit of Web3 auth is that it doesn’t need you to enter your ASP.NET app’s username and password or use an external authentication service. Instead, it is the same mechanism used to log you into your Ethereum account, making it safe and easy.
Tokens for securing REST APIs
The JWT (JSON Web Token) is an open standard extension of OAuth 2.0 for creating access tokens that assert certain claims.
JWTs can be used in a variety of different scenarios, compared to API keys and OAuth tokens that are always used to access APIs. One reason for this is that it can store just about any type of data. It, therefore, excels in combination with OAuth
Functions of a JSON Web Token:
- Authentication: When a user logs in, a JWT is returned and stored in local storage or as a cookie. This is the most common function of a JSON Web Token. It is similar to how a JWT will be used to authenticate a user after they log into their Ethereum account.
- Information transfer: JWTs can do more than just authenticate a user. They can securely transmit information between two endpoints. This is the other part of our use case that’s relevant. Since we require the user to sign a text message using their private key, the token can carry this information as well and allow the user to get authenticated.
Additional Sources
Author




Leave a Comment