Imagine a company grappling with significant delays due to employees' inability to access the necessary software and applications. This challenge stems from poor and inconsistent access provisioning, which not only leads to frustration but also results in lost productivity. Furthermore, employees often find themselves without access to the right tools for their work, exacerbating the issue.
However, everything changed when the company implemented automated access provisioning. This transition eliminated the previous challenges, granting employees instant access to the applications they required. As a result, operations began to run smoothly, enhancing overall productivity and employee satisfaction.
What is Access Provisioning?
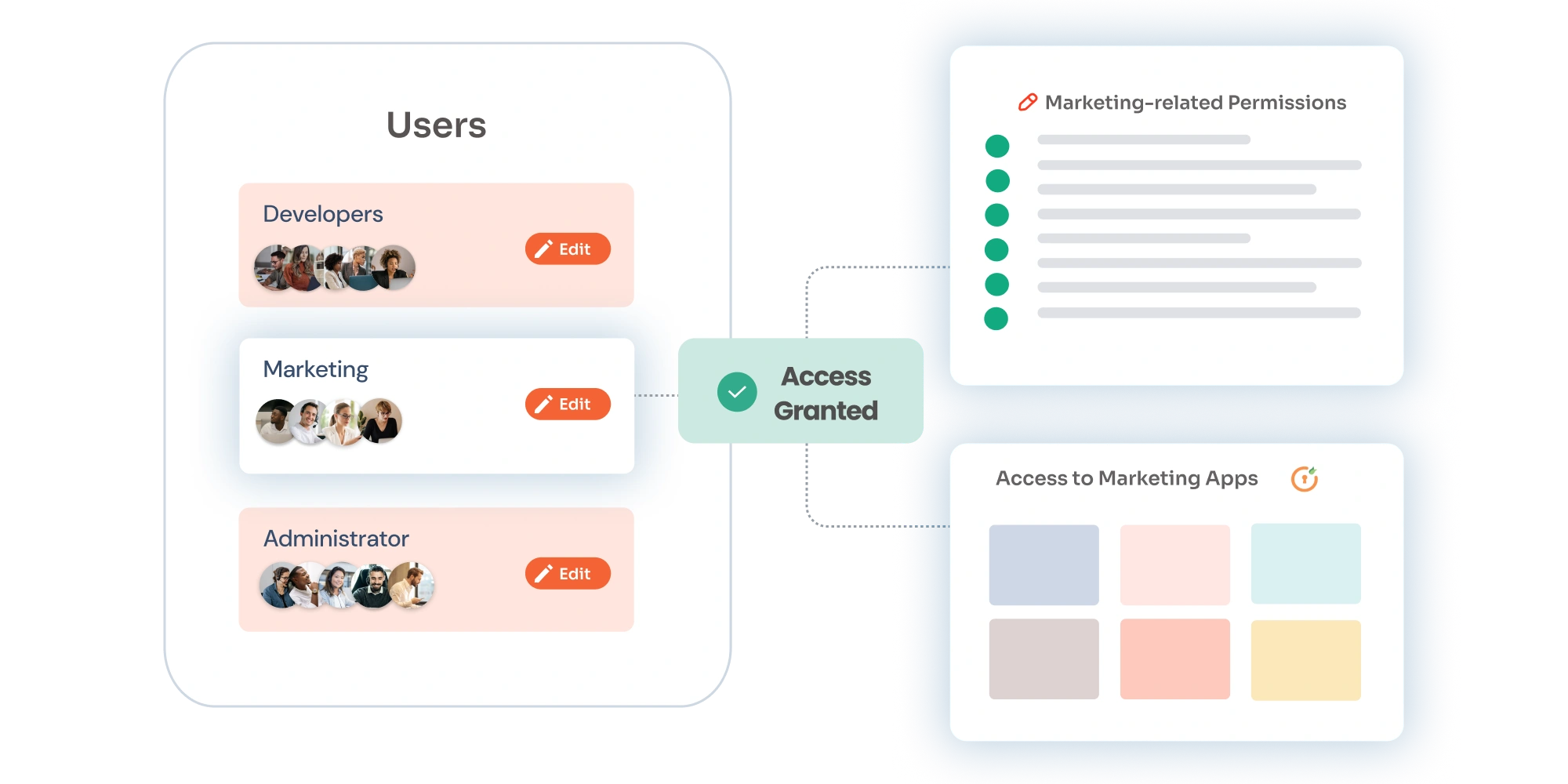
Access provisioning is the process of managing and granting user access to various systems and applications within an organization. It’s crucial for ensuring that the right people have the right access at the right time. This process is especially important in scenarios like onboarding new employees, managing permissions for contractors, or adjusting access when roles change.
This blog educates readers on access provisioning and its importance in enhancing business efficiency and security. It covers best practices and real-life examples of automated access provisioning to demonstrate its value in optimizing workflows.
What are the Methods of Access Provisioning?
Access provisioning refers to the process of granting users the permissions they need to access systems and data. Here are the main types:
1. Discretionary Access Provisioning (DAP)
Discretionary Access Provisioning (DAP) empowers resource owners—such as department heads or team leaders—to determine access permissions for their resources. This method allows for localized control, enabling owners to grant or revoke access based on their discretion. However, while DAP is straightforward and cost-effective, it presents several challenges:
- Inconsistency: Different resource owners may apply varied standards, leading to discrepancies in access management.
- Human Error: Manual processes increase the risk of mistakes, which can compromise security.
- Scalability Issues: As organizations grow, DAP may struggle to efficiently manage increased user bases without a robust identity and access management (IAM) framework.
- Compliance Risks: This method may not adequately meet regulatory requirements due to its ad hoc nature.
2. Self-Service Access Provisioning (SAP)
Self-Service Access Provisioning (SAP) enables users to autonomously request access to necessary resources without requiring IT approval. This approach streamlines the provisioning process by allowing users to select their desired access rights, significantly reducing delays associated with traditional approval workflows. The benefits include:
- Increased Efficiency: Users can quickly gain access to required resources, enhancing productivity.
- Reduced IT Burden: By minimizing the number of requests that require IT intervention, SAP allows IT teams to focus on more critical tasks
3. Workflow-Based Access Provisioning (WAP)
Workflow-Based Access Provisioning (WAP) employs a structured approval process for granting access. Requests undergo a series of predefined stages where designated approvers validate them before access is granted. This method enhances accountability and compliance by ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized personnel. Key features include:
- Hierarchical Approval: Access requests may require validation from multiple levels of management, reinforcing security protocols.
- Audit Trails: WAP facilitates tracking of who approved what and when, aiding in compliance audits and investigations
4. Automated Access Provisioning
Automated Access Provisioning leverages software tools to manage user permissions based on established rules and policies. This method significantly reduces manual intervention, thereby minimizing errors and expediting the provisioning process. Notable advantages include:
- Consistency: Automated systems ensure uniform application of access policies across the organization.
- Scalability: Automation allows organizations to efficiently manage growing user bases without compromising security.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Automated systems can dynamically adjust permissions based on changing user roles or conditions, enhancing security posture.
These methods help organizations manage user access efficiently while ensuring security and compliance. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific needs and structure of the organization.
How to Automate Access Provisioning?
Automating access provisioning is a game-changer for organizations looking to streamline user management, boost productivity, and tighten security. By replacing manual processes with automated workflows, businesses can ensure users get the right access at the right time while reducing errors and risks. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you implement automated access provisioning effectively.
Challenges with Manual Processes:
Manual access provisioning can be tedious and fraught with inefficiencies. Here’s where things often go wrong:
- Delays and Security Gaps: Onboarding and offboarding users manually can take time, leaving new hires without access or former employees with lingering permissions that could pose security threats.
- Incorrect Permissions: It’s easy to grant too much or the wrong type of access when doing it manually. This not only violates the principle of least privilege but also exposes critical systems to unnecessary risks.
- Complicated Management: Keeping track of who has access to what across multiple applications is a logistical nightmare, especially as organizations grow and adopt more tools.
Steps to Automate Access Provisioning:
Here’s how you can modernize your access management process with automation:
- Integrate with HR Systems Start by connecting your Identity and Access Management (IAM) platform to your HR system. This integration ensures that user lifecycle events—like onboarding, promotions, departmental transfers, or terminations—trigger automatic updates in access permissions. For example:
- When a new hire is added to the HR system, they’re automatically provisioned with the appropriate accounts and permissions based on their role.
- When an employee leaves, their access is revoked immediately, eliminating potential security risks.
- Define Role-Based Access
Establish clear policies using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). By mapping roles (e.g., "Sales Manager" or "IT Support Specialist") to specific permissions, you ensure that users automatically receive the exact level of access they need—nothing more, nothing less. This approach simplifies provisioning while adhering to the principle of least privilege, a key security best practice. - Leverage APIs or SCIM for Seamless Integration
Use APIs or SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management) protocols to enable smooth communication between your IAM system and target applications. These technologies allow you to:
- Automatically create, update, or deactivate user accounts across multiple platforms in real time.
- Maintain consistency across systems without manual intervention.
For example, if an employee changes roles, SCIM can instantly update their permissions across tools like Salesforce, Slack, or cloud storage platforms.
- Implement Automated Workflows
Set up workflows that handle repetitive tasks like approvals, notifications, and audits. For instance:
- A new hire’s manager can approve their access request through an automated workflow without needing IT involvement.
- Notifications can alert stakeholders when access is granted or revoked.
These workflows not only save time but also ensure compliance by maintaining a clear audit trail of every action taken.
- Monitor and Audit Access
Automation doesn’t mean “set it and forget it.” Regularly review user access levels and audit logs to ensure compliance with internal policies and external regulations (like GDPR or HIPAA). Automated tools can flag anomalies—such as dormant accounts or excessive permissions—so you can address them proactively.
Why Automation Matters?
By automating access provisioning, organizations can:
- Increase Efficiency: Onboard employees faster and eliminate bottlenecks in the approval process.
- Improve Security: Minimize human error and reduce over-provisioning by sticking to predefined rules.
- Ensure Compliance: Maintain detailed logs for audits and meet regulatory requirements effortlessly.
By automating these processes, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce security risks, and ensure that users have the appropriate access at all times.
Stages of Access Provisioning
Access provisioning involves several key stages to ensure that users have the right access to systems and data. Here’s a breakdown of each stage:
- User Onboarding - This is the process of bringing new users into the system. It includes collecting their information and setting up their accounts.
- Role Assignment and Permission Mapping - In this stage, we assign specific roles to users based on their job responsibilities. We also map out what permissions each role has, determining what data and systems they can access.
- Provisioning Access - Here, we grant users the access they need based on their assigned roles. This step ensures they can use the tools and information necessary for their work.
- Access Monitoring and Management - Once access is granted, we continuously monitor how users are using it. This includes updating permissions as needed to reflect any changes in roles or responsibilities.
- Deprovisioning Access - When a user no longer needs access—whether they leave the company or change roles—we remove their access rights to protect sensitive information.
- Auditing and Training -
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular checks to ensure that access levels are appropriate and comply with security policies.
- User Training: Provide training on security best practices to help users understand their responsibilities regarding access.
By following these stages, organizations can manage user access effectively and maintain security.
Benefits of Automating Access Provisioning
- Work Efficiency Automating access provisioning speeds up the process of granting and managing user access. This reduces manual tasks, allowing employees to focus on their core responsibilities. With automation, you can quickly onboard new employees and adjust access as roles change, leading to a more agile workforce.
- Security Automation enhances security by ensuring that access permissions are consistently applied and monitored. It minimizes human error, which can lead to unauthorized access. Automated systems can also quickly revoke access when employees leave or change roles, protecting sensitive information.
- Auditing and Compliance Automated access provisioning simplifies auditing and compliance with regulations. It creates a clear record of who has access to what, making it easier to demonstrate compliance during audits. This transparency helps organizations avoid penalties and maintain trust with clients and stakeholders.
- Additional Benefits
- Cost Savings: Reducing manual processes lowers administrative costs.
- User Experience: Faster access provisioning improves employee satisfaction and productivity.
- Scalability: Automation allows organizations to easily scale their operations without increasing administrative overhead.
In summary, automating access provisioning boosts work efficiency, strengthens security, ensures compliance, and offers additional benefits like cost savings and improved user experience.
Best Practices in Access Provisioning
- Principle of Least Privilege Always grant users the minimum access they need to perform their jobs. This approach minimizes potential damage from accidental or malicious actions and limits the impact of security breaches.
- Regular Audits Conduct frequent reviews of user access rights to ensure they are appropriate. This includes checking for outdated permissions and orphaned accounts, helping to maintain security and compliance.
- Access Certification Regularly verify that users still require their access rights. This process ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information and resources.
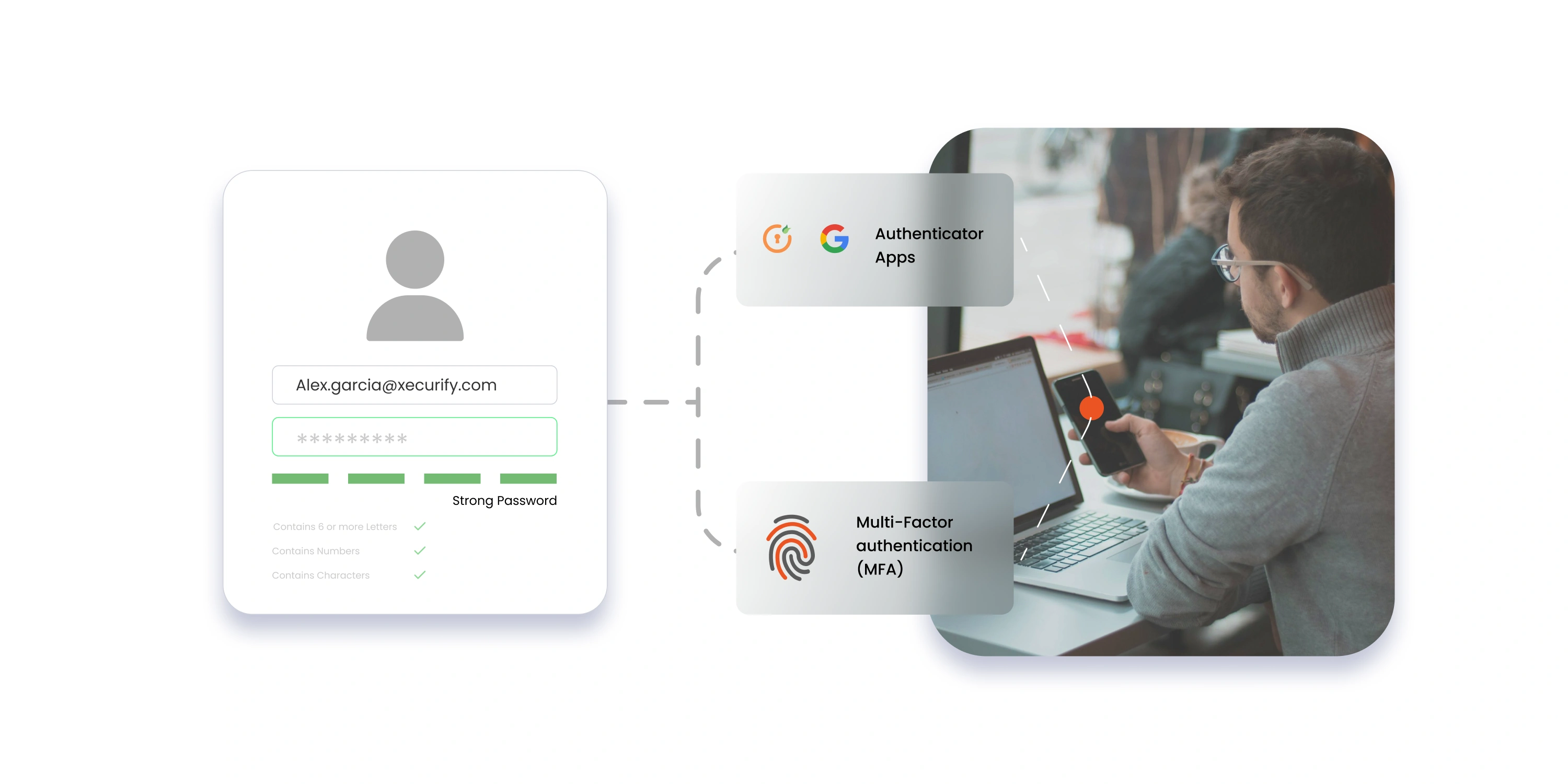
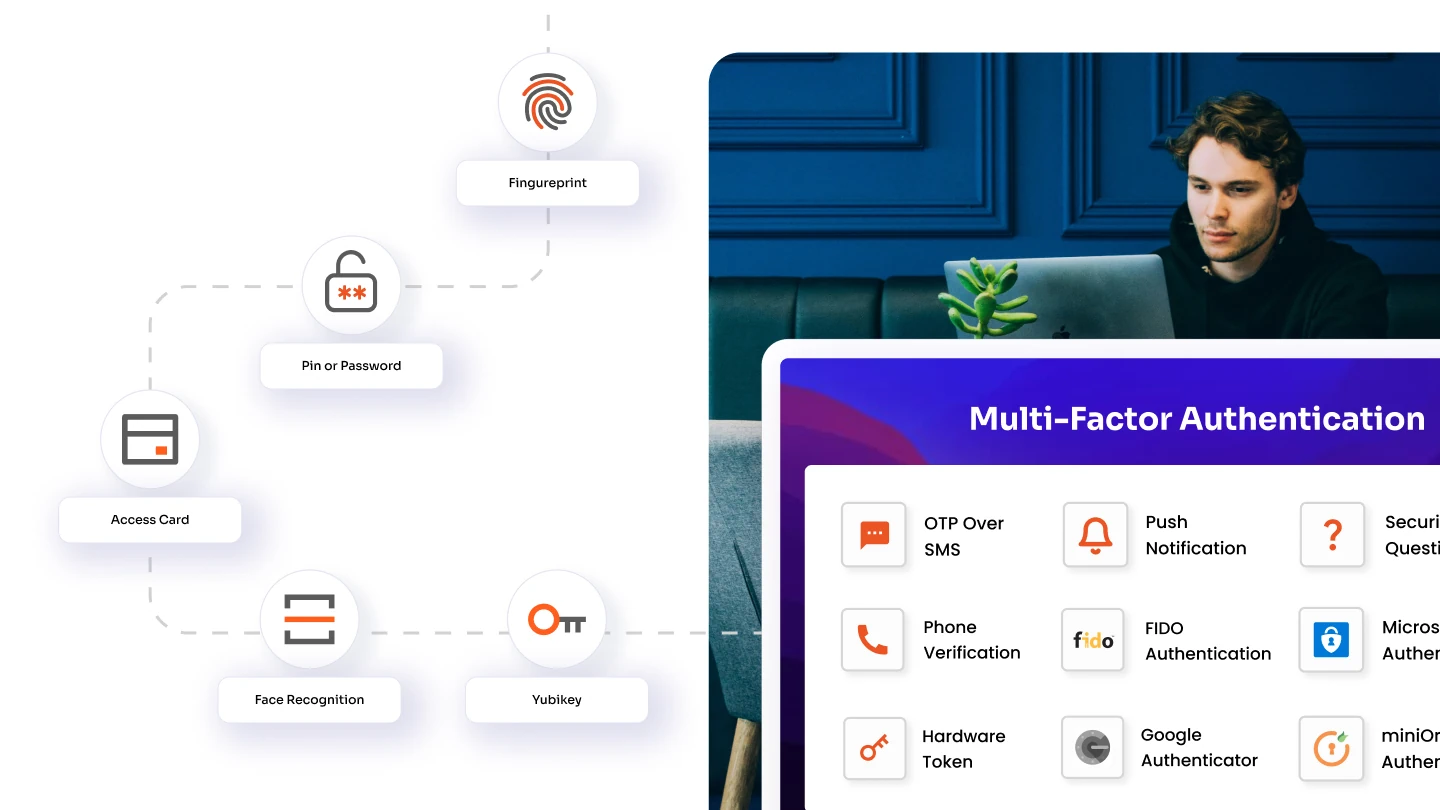
- Strong Authentication Implement robust authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to enhance security. This adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Documentation Maintain clear records of access policies and procedures. Documenting who has access to what resources helps in audits and compliance checks, ensuring accountability.
- Security Awareness Training Educate employees about their role in protecting data and managing access rights responsibly. Regular training can reduce the risk of data breaches caused by human error.
- Automated Provisioning Tools Utilize automated systems for managing user access. These tools streamline the provisioning process, reduce errors, and provide an audit trail for compliance.
By following these best practices, organizations can enhance their security posture while effectively managing user access.
FAQs on Access Provisioning
- How is Access Provisioning Managed in SaaS Platforms?
Access provisioning in SaaS platforms is vital for secure user access management. Access provisioning manages who accesses systems and data, ensuring security and compliance. The process includes onboarding (creating accounts and assigning permissions), ongoing management (updating access as roles change), and offboarding (removing access when users leave or change roles). Common methods include Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which assigns permissions based on roles; Attribute-Based Access Control(ABAC) , which uses user attributes for more granular control; and Tempo, which provides short-term access for contractors or temporary staff. To optimize provisioning, organizations should automate processes, establish clear access policies, conduct regular audits, and integrate Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions. These practices ensure secure data management while maintaining operational efficiency. - What Does Least Privilege Access Mean in Access Provisioning?
Least privilege access in access provisioning is a cybersecurity principle that limits users to the minimum permissions necessary for their job functions. This reduces the organization's attack surface and prevents unauthorized actions by ensuring users have only the essential access needed for their tasks. Key elements of implementing least privilege access include:
- Identity Authentication: Verifies that only authorized users can access systems.
- Device Health Assessments: Evaluates device security before granting access to prevent risks from compromised devices.
- Segmentation: Provides granular control over user-to-application access. By applying least privilege access, organizations can protect sensitive data and critical assets, minimizing risks from external threats and internal misuse. Regular reviews of user permissions help maintain compliance and ensure access aligns with current job responsibilities.
- What is the role of Access Provisioning in Cybersecurity?
Access provisioning is critical in cybersecurity as it controls and manages user access to systems, ensuring only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. It enforces the principle of least privilege, granting users only the permissions needed for their roles, reducing risks like data breaches and insider threats. Key practices include identity authentication, device health checks, and segmentation for granular control. Regular audits of access rights ensure compliance with regulations and maintain security. By managing access effectively, organizations protect sensitive data, minimize risks, and enable secure, efficient operations. - Can temporary access be provisioned in a DevOps environment?
Yes, temporary access can be provisioned in a DevOps environment. This practice allows developers to gain short-term access to resources for tasks such as troubleshooting or testing without compromising security. In cloud platforms like AWS, services such as AWS Security Token Service (STS) enable users to obtain temporary credentials, ensuring secure access without the risks associated with permanent credentials. Similarly, in Azure, developers can use pipelines to grant temporary access to resources, such as adding their public IP addresses for a limited time. Implementing temporary access involves establishing clear policies and using tools like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to manage permissions effectively. Regular audits and automated deprovisioning processes help maintain security by ensuring that temporary access is revoked after use. Overall, this approach enhances security while allowing flexibility in a fast-paced DevOps environment.
Author


Leave a Comment