Adaptive Authentication, also known as Risk-Based Authentication, is a dynamic security approach that evaluates multiple risk factors like user behavior, device, location, and IP reputation during login attempts. Instead of enforcing strict authentication every time, it intelligently adjusts the security requirements based on real-time risk analysis. Low-risk activities allow seamless access, while high-risk actions trigger additional verification steps like Adaptive MFA.
miniOrange’s Adaptive Authentication solution strengthens login security without disrupting the user experience. By applying Risk-Based Authentication policies, miniOrange ensures that only legitimate users gain access, while potential threats are blocked or challenged with step-up authentication. This flexible security framework not only protects sensitive resources but also reduces unnecessary friction for trusted users.
What is Adaptive Authentication?

Traditional authentication methods, including Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), require users to provide specific credentials each time they attempt to log in. While MFA strengthens security by adding layers like one-time passcodes or authenticator apps, it still follows a static model where the same steps are repeated for every login. This can create vulnerabilities, especially if users' credentials are compromised.
Adaptive Authentication takes a smarter, dynamic approach. Instead of treating every login attempt equally, it adjusts the authentication process based on real-time contextual risk factors such as IP address, device type, location, login time, and user behavior patterns. In low-risk scenarios, users can access resources seamlessly with minimal friction. In high-risk cases, the system enforces additional security measures like Adaptive MFA or blocks access altogether.
By combining Behavioral Authentication and Context-Aware Authentication, adaptive systems ensure that authentication requirements are proportionate to the detected risk. Powered by Risk-Based Authentication, miniOrange’s Adaptive Authentication solution intelligently strengthens login security without compromising user experience, making it much harder for attackers to breach corporate systems.
How Does Adaptive Authentication Work?
Adaptive Authentication, also known as Risk-Based Authentication, builds a dynamic user profile based on attributes like geographic location, device type, IP address, and job role. Each time a user attempts to log in, the system analyzes these contextual signals and calculates a real-time risk score.
Depending on the assessed risk, authentication requirements are adjusted. For example, if a user logs in from a trusted device at a usual location, they may gain access seamlessly. However, if an attempt is made from an unknown device or an unusual location, the system may trigger additional steps such as device registration, answering security questions, or enforcing Adaptive MFA to verify identity.
By continuously evaluating context and behavior, Adaptive Authentication strengthens security without disrupting legitimate user activity, ensuring smarter access control based on real-world risk factors.
Key Components of Adaptive MFA
- Contextual Factors: Adaptive MFA evaluates multiple context signals such as the user's geographic location, registered device, IP address, and time of access. Any deviation from the normal pattern triggers additional authentication measures.
- Behavioral Biometrics: The system also analyzes subtle user behaviors like typing speed, mouse movements, and touch dynamics. These behavioral patterns help differentiate between legitimate users and potential attackers without intrusive prompts.
- Risk Scoring: Every authentication attempt undergoes real-time risk analysis. Based on the calculated risk score, the system decides whether to allow seamless access or enforce step-up authentication methods like additional MFA challenges.
Benefits of Adaptive Authentication
Here are some benefits of Adaptive Authentication
- Stronger Data Security: Shields corporate systems and sensitive information from unauthorized access by dynamically adjusting security measures based on risk.
- Seamless Integration: Easily integrates with existing IT infrastructure while offering flexible, dynamic policy enforcement across applications and user groups.
- Real-Time Access Control: Continuously evaluates login risk and adapts access requirements instantly, enhancing security without manual intervention.
- API-Driven Protection: Extends adaptive authentication and enhanced security across cloud-based applications through simple API integrations.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Supports a wide range of devices and browsers, ensuring secure access for users regardless of their platform.
- Smooth User Experience: Embeds adaptive security measures without disrupting workflows, maintaining user productivity while strengthening defenses.
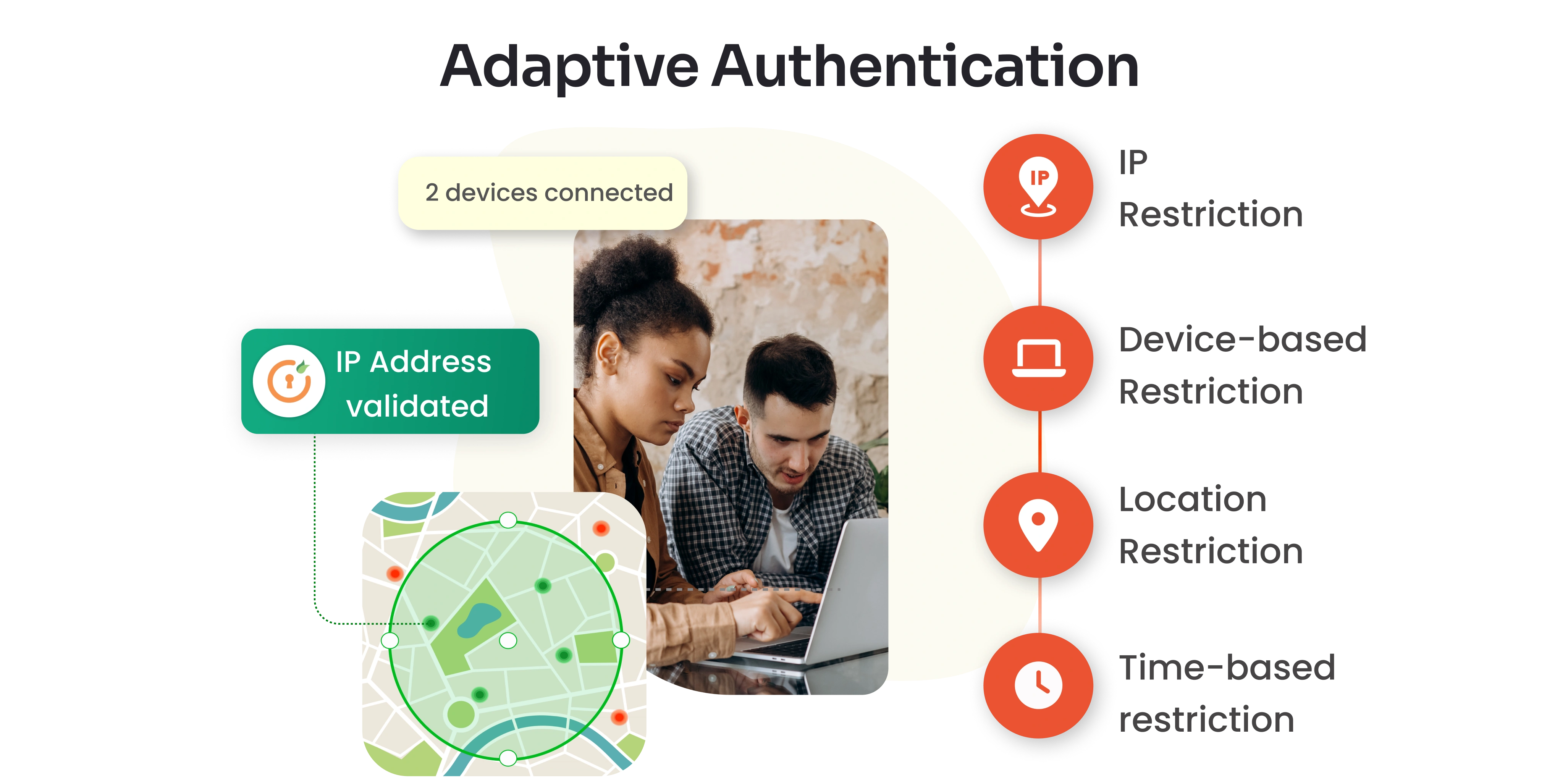
Adaptive Authentication Methods
- IP-Based Restriction: Administrators define trusted or restricted IP address lists. Login attempts are evaluated against these lists to determine whether access is granted, challenged, or denied.
- Location-Based Restriction: Users are allowed to log in only from approved geographic locations. Attempts from unauthorized locations may trigger additional authentication or be blocked.
- Device-Based Restriction: Only registered and trusted devices are permitted for login, minimizing the risk of unauthorized device access.
- Time-Based Restriction: Access is limited to predefined time windows or zones. Login attempts outside these parameters are either challenged with additional authentication steps or denied altogether.

Adaptive Authentication and Machine Learning
Modern Adaptive Authentication solutions harness the power of machine learning to enhance both security and user experience. By continuously learning from user behavior, such as device usage patterns, login times, geographic locations, and IP reputation, these systems build a behavioral baseline for every user.
When a login attempt deviates from the expected behavior, behavioral authentication techniques powered by machine learning assign a dynamic risk score. Based on this score and according to IT-defined policies, the system triggers context-specific responses such as adaptive MFA challenges or access denial.
Advanced Risk-Based Authentication solutions like miniOrange integrate AI and machine learning to monitor authentication events in real time, automatically detecting unusual patterns and potential threats—ensuring faster, smarter protection for critical resources.
Conclusion
Adaptive Authentication is no longer a luxury; it is a critical need in today’s complex cybersecurity environment. By dynamically adjusting security measures based on real-time risk signals like user behavior, device type, and login patterns, an advanced authentication solution ensures enhanced protection without compromising user experience. To truly secure access, it is important to understand the difference between Authentication vs Authorization. While authentication verifies the user’s identity, authorization governs what actions they are permitted to take.
Adaptive Authentication strengthens the authentication step, ensuring only verified users move forward to access sensitive resources. Organizations that invest in risk-based authentication and adaptive MFA not only protect their systems but also prepare for evolving threats. Ready to implement intelligent, context-aware security? Contact Us to explore a tailored solution for your organization. Book a 30 Days Free Demo today and see adaptive security in action!
FAQs
1. Is adaptive authentication the same as risk-based authentication?
Yes, adaptive authentication and risk-based authentication are closely related. Both involve evaluating the risk level of each login attempt in real time based on contextual factors like device, location, and user behavior. Depending on the assessed risk, the system adapts authentication requirements, enforcing stronger security measures only when needed.
2. Can I combine adaptive authentication with MFA?
Absolutely. Adaptive authentication often works alongside Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to provide an extra layer of security. In low-risk situations, users may log in with minimal steps, while in higher-risk scenarios, adaptive MFA challenges are triggered automatically, requiring additional verification like OTPs, biometrics, or security questions.
3. Does adaptive authentication affect user experience?
No, it actually improves it. Adaptive authentication ensures that trusted users can access resources seamlessly without unnecessary authentication barriers. Only when a login attempt appears risky does the system introduce additional steps, maintaining a strong balance between security and user convenience.
4. Can users bypass MFA for low-risk scenarios?
Yes, in low-risk scenarios, users can be granted access without triggering an MFA challenge. Adaptive authentication intelligently assesses the risk context, and if everything matches the user's normal behavior and device profile, it allows login with basic credentials while still keeping security intact.
miniOrange
Author




Leave a Comment