With the growing vulnerability of password-only security systems, your applications, devices, and operating systems would need an authentication system that creates foolproof security. Moreover, as vulnerabilities in cyber ecosystems evolved and password breaches became increasingly common, organizations needed stronger authentication methods to protect sensitive data and user accounts. Traditional passwords proved inadequate; they could be easily guessed, stolen through phishing attacks, or compromised in data breaches.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
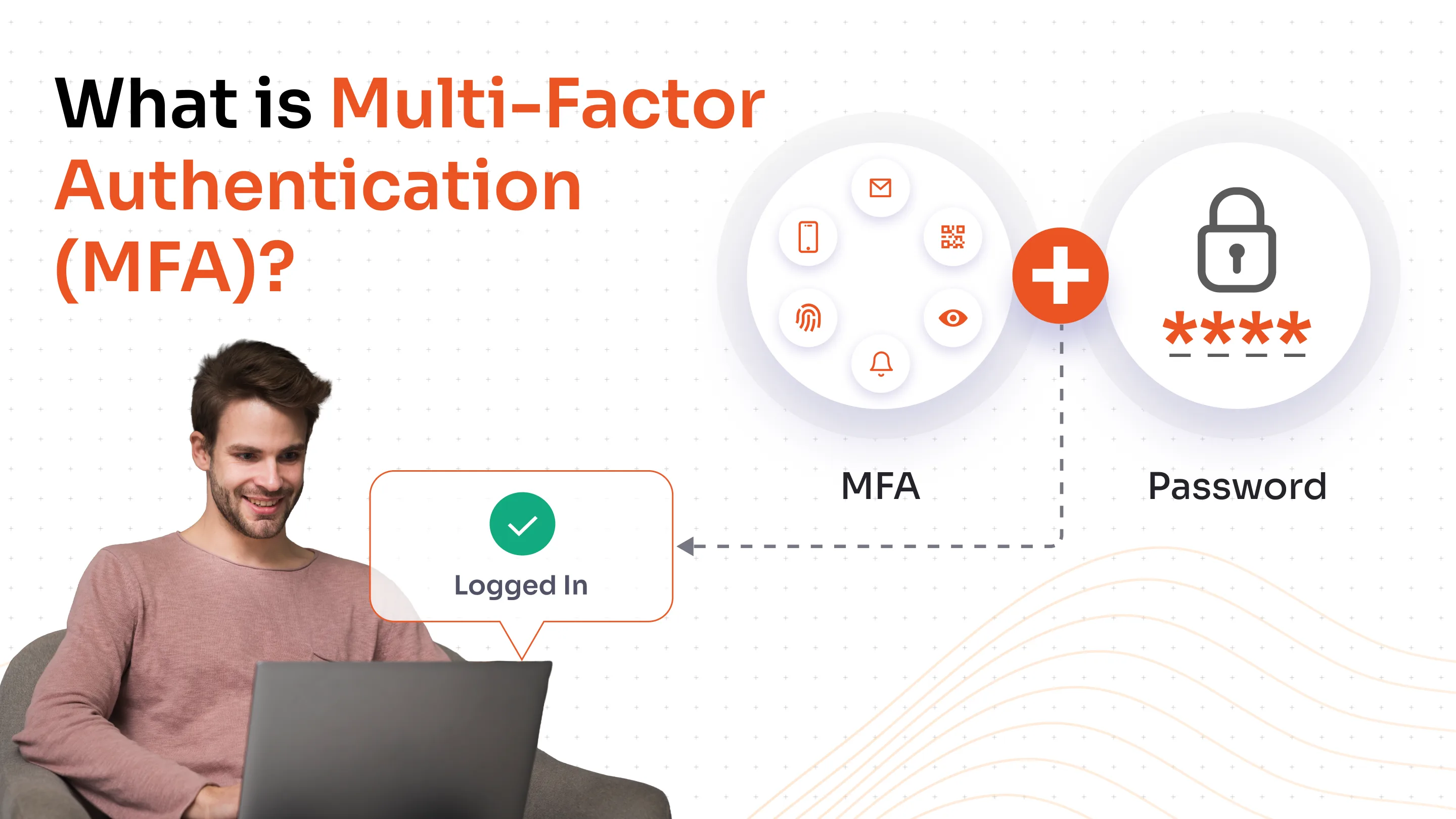
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires users to provide two or more distinct verification factors to gain access to a system, application, or online account. Unlike traditional single-factor authentication that relies solely on passwords, MFA creates multiple layers of defense by combining different types of credentials from independent categories.
The authentication factors typically fall into three main categories: something you know (such as a password or PIN), something you have (like a smartphone, hardware token, or security key), and something you are (such as a fingerprint, facial recognition, or other biometric data). By requiring multiple forms of evidence to verify identity, MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access, even when one authentication factor has been compromised.
Importance of MFA in Modern Cybersecurity
The importance of MFA in modern cybersecurity is paramount. As data breaches and credential thefts continue to rise, traditional password-based authentication has become increasingly vulnerable.
Strengthens Security Against Credential Theft
MFA significantly enhances security by requiring multiple verification factors, making unauthorized access exponentially more difficult. Even if attackers obtain a user's password through phishing, data breaches, or brute-force attacks, they still cannot access the account without the additional authentication factors. According to Microsoft, MFA can prevent 99.9% of automated attacks on accounts, demonstrating its effectiveness as a critical defense mechanism in today's threat landscape.
Protects Against Phishing and Social Engineering
MFA provides robust protection against phishing attacks, one of the most prevalent cyber threats facing organizations today. Even when users inadvertently reveal their passwords to fraudulent websites or malicious actors, the additional authentication layers required by MFA prevent attackers from gaining account access. This protection is especially crucial as phishing techniques become increasingly sophisticated and difficult for users to detect.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance and Data Protection
Implementing MFA helps organizations meet stringent regulatory and compliance requirements related to identity assurance and data protection. Many industry standards and regulations, including HIPAA and other data protection frameworks, now mandate multi-factor authentication for accessing sensitive systems and data. By deploying MFA, businesses demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer information and reducing the risk of costly data breaches that can result in legal penalties and reputational damage.
Reduces Organizational Security Costs
While MFA requires an initial investment, it proves far more cost-effective than dealing with the aftermath of security breaches. Data breaches can cost organizations millions in remediation, legal fees, regulatory fines, and lost customer trust. MFA minimizes these risks by preventing unauthorized access at the authentication stage, reducing incident response costs, and protecting business continuity.
Enables Secure Digital Transformation
MFA empowers organizations to confidently pursue digital initiatives, cloud adoption, and remote work strategies without compromising security. By implementing adaptive MFA that adjusts security requirements based on risk factors like location, device, and user behavior, businesses can balance security with user experience. This flexibility allows companies to support remote employees, enable secure access to cloud resources, and facilitate digital transactions while maintaining robust security controls.
Common factors used in MFA
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple independent factors before gaining access to systems or data.
Something you know represents knowledge-based credentials like passwords, PINs, or security question answers. These are the most common but also the most vulnerable to phishing and social engineering attacks.
Something you have involves physical possession of authentication devices. This includes hardware security tokens (like YubiKeys), one-time passcodes (OTPs) delivered via SMS to registered phones, or time-based codes generated by authenticator apps such as Google Authenticator or miniOrange Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator. Push notifications to mobile devices also fall into this category.
Something you leverages unique biometric characteristics, including fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, or voice patterns. Modern smartphones and enterprise systems increasingly incorporate biometric authentication due to its convenience and difficulty to replicate.
By combining two or more of these factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if one factor becomes compromised. This layered approach is essential for protecting sensitive business systems and data.
MFA Authentication Process
MFA solution follows a structured sequence of verification steps to ensure secure access to systems and applications.
Step 1: Initial Credential Entry
The user enters their primary credentials, typically a username and password, into the login interface of the application or system.
Step 2: First Factor Verification
The system validates the username and password against stored credentials in the authentication database to confirm the user's identity claim.
Step 3: Second Factor Prompt
Upon successful password verification, the system immediately triggers a request for an additional authentication factor from a different category (something you have or something you are).
Step 4: Second Factor Delivery
The system sends a one-time passcode via SMS, generates a push notification to a registered device, or prompts for biometric verification depending on the configured MFA method.
Step 5: User Response
The user provides the requested second factor by entering the OTP, approving the push notification, scanning their fingerprint, or inserting a hardware token.
Step 6: Factor Validation
The system verifies the authenticity and validity of the second factor, checking for correct codes, biometric matches, or token signatures.
Step 7: Access Grant or Denial
Access is granted only when all required factors are successfully authenticated; otherwise, the login attempt is denied and logged for security monitoring.
Common MFA Methods
Organizations can choose from various MFA methods, each offering different levels of security and user convenience.
Text Messages (SMS) or Voice Calls
A temporary one-time password (OTP) is generated by the authentication server and sent to the user's registered phone number via SMS or delivered through an automated voice call. The user enters this time-limited code to complete authentication. While convenient and widely accessible, SMS-based authentication is vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks and message interception, making it the least secure MFA option.
Authenticator Apps
Mobile applications like Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or Authy generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) using cryptographic algorithms. These apps create six to eight-digit codes that refresh every 30 seconds, eliminating reliance on cellular networks.
Many authenticator apps also support push notifications, allowing users to simply approve or deny login attempts with a single tap. This method provides stronger security than SMS since the authentication codes are generated locally on the device and never transmitted over networks.
Hardware Security Keys
Physical security devices such as YubiKeys or Titan Security Keys connect to computers or mobile devices via USB, NFC, or Bluetooth. These keys support modern authentication standards like FIDO2 and WebAuthn, providing the highest level of phishing resistance.
Users simply insert or tap their key when prompted during login. Hardware keys use public-key cryptography to verify identity without transmitting sensitive credentials, making them nearly impossible to phish or remotely compromise.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric verification uses unique physical characteristics such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, iris scanning, or voice recognition to confirm user identity. Modern smartphones and enterprise systems increasingly incorporate biometric authentication due to its convenience and difficulty to replicate. Biometric data is typically stored locally on the device to protect privacy, and because everyone has unique physical attributes, this method offers high security when properly implemented.
Email Verification Codes
A one-time code or verification link is sent to the user's registered email address, which must be entered or clicked to complete authentication. This method works well for users without smartphones or in environments where other MFA options are unavailable. However, email-based MFA is only as secure as the email account itself, requiring strong email security practices to prevent compromise.
Hardware Tokens
In token-based authentication, physical display tokens generate time-based or hash-based one-time passwords using pre-coded algorithms without requiring network connectivity. Users read the displayed code from the token device and enter it during login. These tokens, such as OTP c200 or OTP c100, provide secure authentication for environments where mobile devices are restricted or unavailable.
MFA vs. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is actually a subset of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), with the key distinction being that 2FA requires exactly two authentication factors, while MFA encompasses two or more verification methods. Both 2FA and MFA offer significantly stronger security than single-factor authentication, but MFA generally provides more comprehensive protection by adding additional layers of defense.
For most consumer applications like social media, banking, and online shopping, 2FA is often sufficient and provides adequate security without overwhelming users. However, MFA becomes necessary for high-security environments such as corporate systems, healthcare facilities, government agencies, and enterprises handling sensitive data or facing advanced cyber threats, where regulatory compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS mandate multiple authentication factors.
In the MFA vs 2FA differentiation, we conclude that the more authentication factors implemented, the harder it becomes for cybercriminals to breach accounts, even if one or two factors are compromised.
Benefits of Using MFA for Your Organization
Improved Operational Efficiency and Productivity
MFA streamlines access management by integrating seamlessly with Single Sign-On (SSO) systems, allowing users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without repeatedly entering credentials. This combination reduces password reset requests and IT helpdesk tickets, freeing up valuable IT resources for more strategic initiatives.
Flexible and Adaptive Security Policies
Organizations can implement adaptive or risk-based MFA that dynamically adjusts authentication requirements based on contextual factors such as user location, device type, network security, and behavior patterns. For low-risk activities like accessing general resources from trusted devices, users experience streamlined authentication, while high-risk scenarios, such as logins from unfamiliar locations or public networks, trigger additional verification steps.
Enhanced Visibility and Access Monitoring
MFA provides comprehensive audit trails and detailed logging of authentication attempts, enabling security teams to monitor access patterns, detect anomalies, and respond quickly to suspicious activities. Organizations gain valuable insights into who is accessing what resources, when, and from where, supporting forensic investigations and improving overall security posture.
Building Confidence and Reputation
Implementing MFA demonstrates a proactive commitment to security, significantly enhancing customer trust and loyalty in an era where data privacy concerns are paramount. Organizations that visibly protect user accounts reduce customer anxiety about data breaches and identity theft, differentiating themselves from competitors who rely solely on password protection.
Future of MFA
Trends in passwordless authentication
The future of multi-factor authentication is defined by passwordless technologies, artificial intelligence, and adaptive security frameworks that prioritize both robust protection and seamless user experiences.
According to Gartner, 60% of large enterprises will phase out password-based authentication by 2025, embracing biometrics, passkeys, and FIDO2-compliant hardware tokens instead. Tech leaders like Microsoft and Google are already offering passwordless login options across their platforms, signaling an industry-wide shift.
Role of AI and behavioral biometrics
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing MFA through context-aware authentication that analyzes user behavior, location, device type, and login patterns to dynamically assess risk levels. These AI-powered systems can detect anomalies such as logins from unfamiliar locations and automatically trigger additional verification layers, reducing fraud incidents by up to 80% according to Forrester Research.
Evolving standards and technologies
Biometric authentication continues to evolve beyond fingerprints and facial recognition to include advanced modalities, such as iris scanning, behavioral biometrics that analyze typing patterns and mouse movements, and multi-modal approaches combining voice and fingerprint verification.
Additionally, blockchain-based decentralized identity solutions are gaining traction, enabling users to securely control their digital credentials. The adoption of Zero Trust security models incorporating continuous authentication ensures real-time user verification throughout sessions rather than one-time login checks.
Conclusion
Multi-factor authentication has evolved from an optional security enhancement to an essential safeguard in today's threat landscape. As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated and data breaches continue to escalate, organizations can no longer rely solely on passwords to protect sensitive systems and information. Implementing multi-factor authentication software significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, prevents credential theft, and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
FAQs
What is meant by multi-factor authentication?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process requiring users to provide two or more verification factors, such as passwords, security codes, or biometric scans, to access accounts or systems. This layered approach makes unauthorized access significantly more difficult, even if one factor is compromised.
Is MFA the same as 2FA?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a subset of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). While 2FA requires exactly two verification factors, MFA encompasses any authentication using two or more factors. Essentially, all 2FA is MFA, but MFA can include three or more factors for enhanced security.
How do I know if my MFA is enabled?
Check your account's security settings for labels like "Two-Step Verification" or "Multi-Factor Authentication". When enabled, you'll be prompted for additional verification beyond your password during login, such as codes or biometric scans. If you only enter a password, MFA isn't active.
What are the benefits of using MFA?
MFA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks, prevents unauthorized access even when passwords are compromised, and ensures regulatory compliance. It reduces security costs, builds customer trust, and integrates with Single Sign-On for improved efficiency while providing adaptive security.





Leave a Comment