What is SAML?
SAML - Security Assertion Markup Language, it is an XML standard that allows secure web domains to exchange user authentication and authorization data. Using SAML 2.0, an online Service Provider (SP) can contact a separate online Identity Provider (IDP) to authenticate users who are trying to access secure content.
SAML 2.0 authentication protocol is popular for browser-based enterprise applications. SAML 2.0 uses XML data format to transfer messages between applications. This XML document is digitally signed by the Identity Provider and shared with the Service Provider (SP) during the user authentication process.
Basics Of SAML
1. SAML Service Provider (SP): A SAML Service Provider (SP) is a system entity that receives and accepts authentication assertions in conjunction with a Single Sign-On (SSO) profile of the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML).
2. SAML Identity Provider (IDP): A SAML Identity Provider (IDP) is a system entity that issues authentication assertions in conjunction with a single sign-on (SSO) profile of the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML). An Identity Provider performs the authentication that the end user is who they say they are and sends that data to the Service Provider along with the user’s access rights for the service.
3. SAML Request: A SAML Request, also referred to as an authentication request, it is generated by the Service Provider (SP) to "request" an authentication.
4. SAML Response: A SAML Response is generated by the Identity Provider (IDP). It contains the actual assertion of the authenticated user. In addition, a SAML Response may contain additional information about the user, such as user profile information, group/role information, etc.
SAML Single Sign-On (SSO)
SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication process in which a user is provided access to multiple applications and/or websites by using only a single set of login credentials (such as username and password). This prevents the need for the user to login separately into the different applications.
The user credentials and other identity information is stored and managed by a centralized system called Identity Provider (IDP). The Identity Provider (IDP) is a trusted system which provides access to other websites and applications.
How SAML 2.0 Works
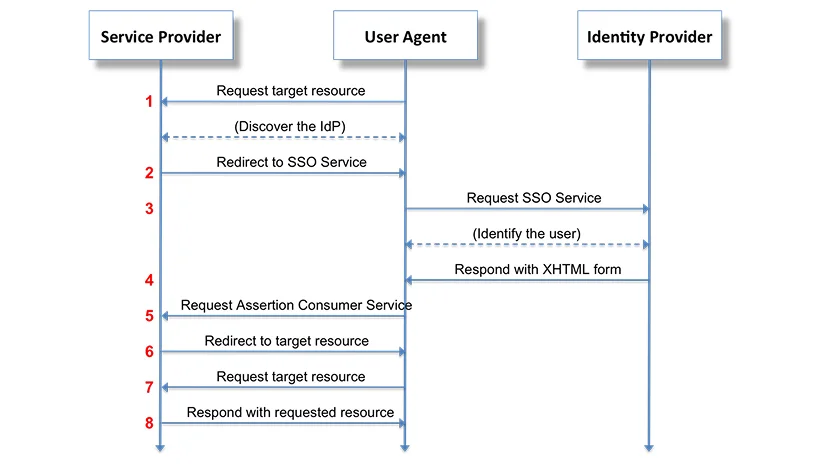
SAML SSO works by transferring the user’s identity from the Identity Provider (IDP) to the Service Provider(SP). This is done through an exchange of digitally signed XML documents. Consider the following Use Case: A user is logged into a system that acts as an Identity Provider(IDP). The user wants to log in to a remote application, i.e. the Service Provider(SP). The following is the flow taking place:
1. The user requests a resource from their desired application/website (Service Provider).
2. The Identity Provider (IDP) verifies the user.
3. The Service Provider identifies the IDP (Identity Provider) and redirects the user back to IDP with authentication request.
4. The Identity Provider sends a response with the XHTML form.
5. Identity Provider (IDP) sends the XML document (SAML Assertion) to the Service Provider (SP) which contains the user authorization.
SAML 2.0 Single Sign-On (SSO) Flow:
Benefits of SAML 2.0 Authentication
- SAML 2.0 Single Sign-On (SSO): SAML provides fastest & efficient access to multiple applications through assertion which helps to connect SAML support Service Provider (SP) to Identity Provider (IDP). SAML 2.0 provides a better user experience through assertion which communicates between the Service Provider (SP) & the Identity Server (IDP).
- Increased Security: SAML authentication eliminates the passwords & provides authentication through digital signature. SAML 2.0 also uses the Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to protect identities from attacks. SAML SSO provides a single point of authentication, which happens at a secure Identity Provider (IDP). Then, SAML transfers the identity information to the Service Providers (SP). This form of authentication ensures that credentials are only sent to the IDP (Identity Provider) directly.
- Reduce Password recovery time: SAML SSO will eliminate password issues such as reset and recovery, which will reduce the time to recover old passwords.
- Reduced costs for the Service Provider (SP): With SAML SSO you don't have to maintain an account for multiple services. The Identity Provider (IDP) will burden this.
- Improved User experience: Without any authentication, a user can access multiple Service Providers by signing in just once which allows a faster and better experience at each Service Provider (SP).
- Standardization: SAML 2.0 interoperates with any system independent of implementation because of its standardized format.
- Loose Coupling of Directories: SAML does not require maintaining and synchronizing user information between directories.
SAML Assertion
SAML 2.0 Assertion is a XML document provided by Identity Provider (IdP) to the Service Provider (SP) which contains the user authorization. SAML 2.0 assertions contain all the information necessary for a Service Provider (SP) to confirm user identity, including the source of the assertion, the time it was issued, and the conditions that make the assertion valid. There are three types of SAML Assertions.
- Authentication Assertion: The specified subject was authenticated by a particular means at a particular time. This kind of statement is typically generated by a SAML authority called an Identity Provider, which is in charge of authenticating users and keeping track of other information about them.
- Attribute Assertion: The specified subject is associated with the supplied attributes.
- Attribute Decision Assertion: A request to allow the specified subject to access the specified resource has been granted or denied.
An assertion consists of one or more statements. For single sign-on, a typical SAML assertion will contain a single authentication statement and possibly a single attribute statement. Note that a SAML response could contain multiple assertions, although it's more typical to have a single assertion within a response.
The SAML specification defines three roles:
- The principal (typically a user)
- The Identity Provider (IDP)
- The Service Provider (SP)
In the use case addressed by SAML, the principal requests a service from the Service Provider (SP). The Service Provider requests and obtains an identity assertion from the Identity Provider (IDP). Based on this assertion, the Service Provider (SP) can make an access control decision - in other words it can decide whether to perform some service for the connected principal.
SAML 2.0 Example
How to configure miniOrange Self-Service Console as a Service Provider by accepting a SAML assertion generated by the miniOrange IDP.
- Register a Service Provider on the Identity Server:
- Add Issuer as miniOrange.
- Assertion Consumer URL as https://login.xecurify.com/moas/samlresponse
- Make sure Enable Attribute Profile is checked.
- Add email address in Attribute Claims.
- Make sure Include Attributes in the Response Always is checked.
- User selects SAML SSO from End User Sign In window to login using miniOrange Identity Server.
- miniOrange Authentication Service sends an authentication SAML request along with Attribute Query to miniOrange Identity Server along with the Consumer Index generated after registering miniOrange as a Service Provider on the Identity Server.
- miniOrange IDP parses the SAML request and redirects to Identity Server Login page.
- User enters the username & password. If valid credentials are entered, IdP sends an encoded SAML Response to the miniOrange Authentication Service with the email address of the user.
- miniOrange Authentication Service receives SAML response, decodes it, parses the email ID of the user. If a valid email address is found, it logs in the user into self-service console.
Also, you can configure miniOrange Self-Service Console as a Service Provider (SP) with Other Identity Providers (IDPs) like Okta, OneLogin, Azure AD, Auth0 etc.
SAML vs. OAuth
OAuth is a slightly newer standard that was co-developed by Google and Twitter to enable streamlined internet logins. OAuth uses a similar methodology as SAML to share login information. SAML 2.0 provides more control to enterprises to keep their SSO logins more secure, whereas OAuth is better on mobile and uses JSON. Facebook and Google are two OAuth providers that you might use to log into other internet sites.
| Feature | SAML 2.0 | OAuth |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | SAML is an authentication protocol. | OAuth is an authorization protocol. |
| Usage Scenario | SAML 2.0 will be used by those who are looking for federation and identity management. They will use this identity to login the users to different applications. | OAuth will be used by those who are not looking to maintain identities but are rather trying to leverage the implementation of secure protocol by applications such as Google, Microsoft, Paypal, who ensure that the identities are authentic. |
| Suitable Application | SAML 2.0 is popular for browser-based applications. | OAuth is suitable for both browser and mobile applications. |
| Commonly Used By | SAM 2.0 is widely used for enterprise applications. | OAuth is widely used for customer applications and API access. |
| Data Format | SAML 2.0 uses XML to transfer messages between applications. | OAuth uses JSON to transfer messages between applications. |




Leave a Comment