Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Cyberattacks strike every 39 seconds worldwide. The stakes are high, making advanced security measures essential. In 2023, businesses faced an average cost of $4.24 million per data breach. Identity and Access Management (IAM) mitigates these risks. Ever wondered how companies keep their data safe from unauthorized access? This article sheds light on IAM's core concepts, benefits, and implementation strategies.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) secures digital identities through policies, processes, and technologies. It authenticates users and authorizes access to resources, ensuring the right individuals access the right resources at the right times for the right reasons. Effective IAM strategies protect organizations from unauthorized access.

Weak or stolen credentials cause 80% of data breaches, making Identity and Access Management (IAM) essential for protecting sensitive information. Implementing IAM boosts security, ensures compliance, improves operational efficiency, and saves costs for organizations.
To secure access and protect sensitive data, you must understand IAM standards like SAML, OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and FIDO.
A robust IAM architecture begins with securing cloud and on-premise environments. Here’s a streamlined guide:
1. Understand Your Application Portfolio: List all applications to identify specific IAM requirements.
2. Create a Logical User Directory: Integrate on-premises directories with cloud services for a unified view.
3. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign roles based on the principle of least privilege.
4. Leverage Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security with multiple factor authentication (MFA) methods.
5. Automate Identity Lifecycle Management: Automate provisioning and de-provisioning to reduce human error.
6. Monitor and Audit Access: Regularly monitor access to ensure compliance and detect suspicious activities.
7. Integrate with Cloud Services: Use cloud-native IAM solutions like AWS IAM, Azure AD, and Google Cloud IAM.
8. OSA Design Pattern:
9. Educate and Train Users: Conduct regular training on IAM architecture best practices.
By following these steps and incorporating the OSA design pattern, you can enhance security and operational efficiency in your IAM architecture.
Understanding how an Identity and Access Management (IAM) system works is essential for protecting sensitive information. From user registration to ongoing monitoring, IAM systems ensure that only authorized users have access to critical resources, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Around 74% of organizations are using Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions to keep track of who has access to what. With the IAM market expected to hit $18.5 billion by 2024, it’s clear that having a solid IAM strategy is crucial for protecting sensitive data and staying compliant with regulations.
Identity management solutions are essential for ensuring that the right individuals have access to the right resources at the right times for the right reasons. These solutions help organizations manage user identities and control access to critical information. Key benefits include:
Access management solutions focus on controlling who can access specific resources and under what conditions. These solutions ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information and systems. Key features include:
Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies the user experience by allowing users to log in once and gain access to multiple applications without needing to re-enter credentials. Key advantages include:
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access. Key benefits include:
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) assigns permissions to users based on their roles within an organization. This approach simplifies access management and ensures that users have the appropriate level of access. Key benefits include:
Privileged Access Management (PAM) focuses on securing and managing privileged accounts, which have elevated access rights. Key features include:
Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) provides cloud-based identity management solutions, offering scalability and flexibility. Key benefits include:
Identity federation allows users to access multiple systems and applications using a single set of credentials, typically through a trusted third-party identity provider. Key advantages include:
By implementing these IAM solutions and technologies, organizations can enhance security, improve compliance, and streamline access management.
These on-premise IAM solutions are hosted within an organization’s data centers, offering high control and customization. They are ideal for industries with stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring data sovereignty and compliance. However, they require significant infrastructure investment and dedicated IT staff, and scalability is limited by physical infrastructure.
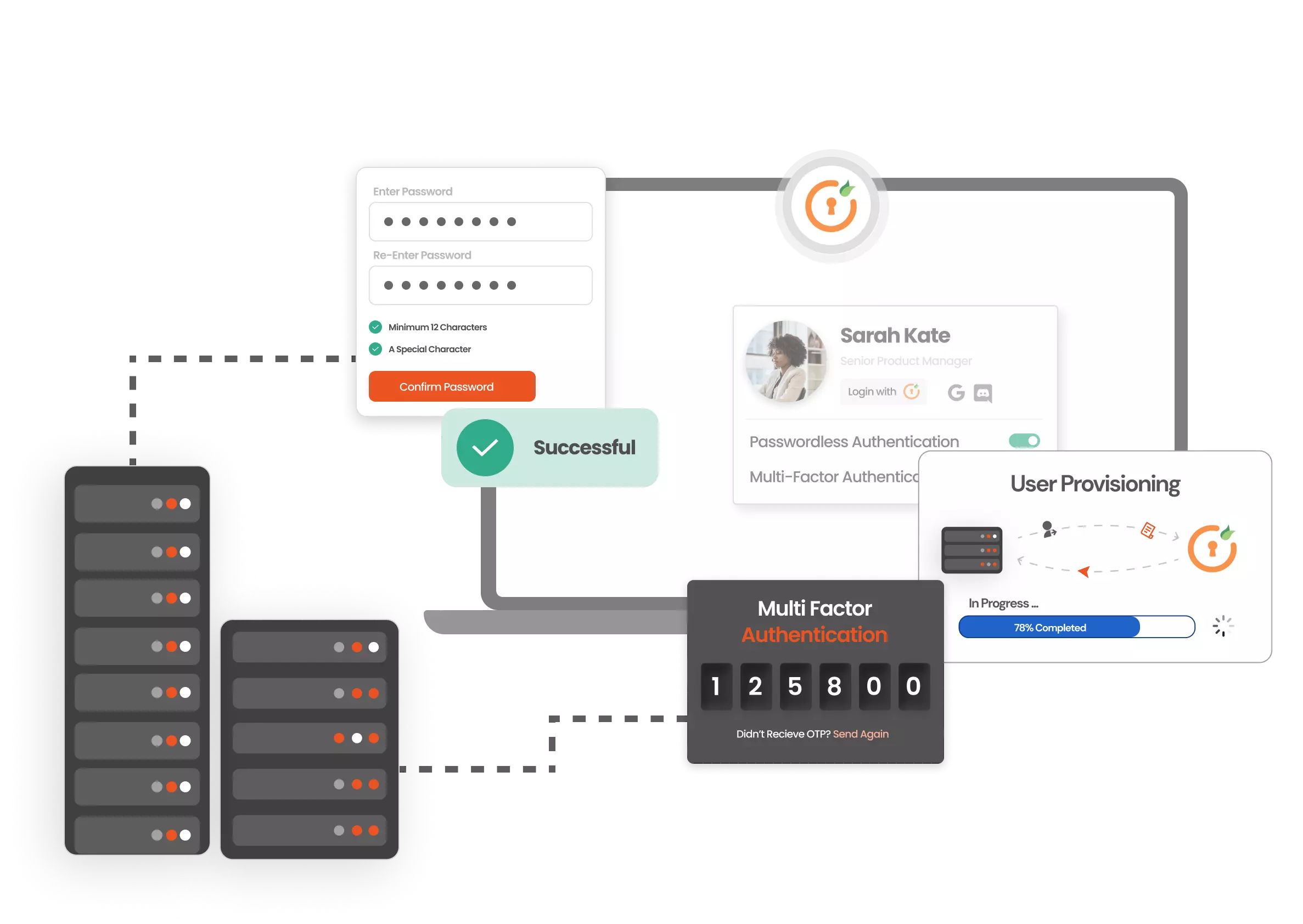
Managed by third-party providers, these cloud IAM solutions offer scalability, ease of deployment, and lower upfront costs. They are perfect for organizations aiming to enhance agility and reduce IT overhead. Key considerations include reliance on third-party security, data privacy, and integration with existing systems.
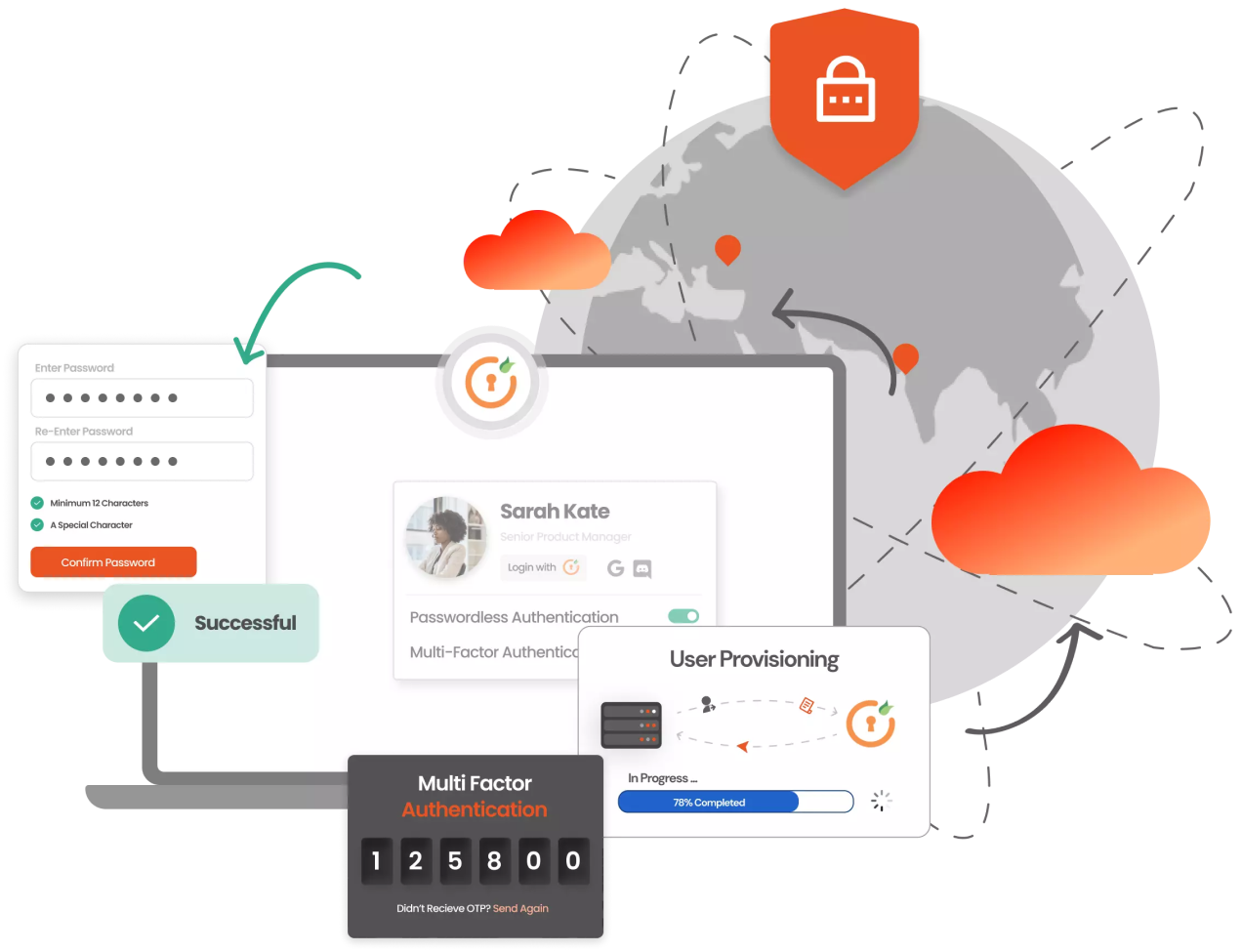
Combining on-premises and cloud-based systems, hybrid IAM provides flexibility and resilience. This approach supports digital transformation by allowing phased migration to cloud-based IAM while maintaining legacy systems. Challenges include managing dual environments and ensuring data consistency and security.
Aspect |
Cloud IAM |
On-Premise IAM |
| Control |
Managed by third-party vendors, less direct control |
Full control over infrastructure and data |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, can easily adjust to changing needs |
Limited by physical hardware and infrastructure |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | A cost-effective solution, providing more features at competitive pricing. Hence, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is low. |
Pricing is usually higher with respect to the features provided. Hence, resulting in increasing TCO. |
| Cost | Subscription-based, operational expenses |
Capital expenditure for hardware and maintenance |
| Implementation Time | Faster deployment, minimal setup required |
Longer deployment time, extensive setup and configuration |
| Maintenance | Handled by service provider |
Requires in-house IT team for maintenance and updates |
| Security | Security managed by vendor may have shared responsibility |
Full responsibility for security can customize security measures |
| Compliance | May need to ensure the vendor meets compliance requirements |
Easier to meet specific regulatory and compliance requirements |
| Customization | Limited customization options |
A high level of customization is possible |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection |
Limited to the organization’s network, may require VPN for remote access |
| Updates | Automatic updates provided by the vendor |
Manual updates are required, managed by in-house team |
| Disaster Recovery | Built-in disaster recovery and backup solutions |
Requires separate disaster recovery and backup plans |
| Integration | Easier integration with other cloud services |
May require custom integration with existing systems |
| Performance | Dependent on internet connectivity and vendor’s infrastructure |
Dependent on the organization’s infrastructure and network |
| Data Sovereignty | Data stored in vendor’s data centers, maybe in different geographical locations |
Data stored within the organization’s physical boundaries |
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: Enhancing security through predictive analytics and automated threat detection.
Passwordless Authentication: Improving user experience and security by eliminating traditional passwords.
Decentralized Identity Management: Empowering users with control over their digital identities using blockchain technology.
Continuous Adaptive Risk and Trust Assessment (CARTA): Dynamically adjusting security measures based on real-time risk assessments.
Implementing a robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) strategy is essential for securing your enterprise. Start by conducting a thorough identity and access audit to identify potential vulnerabilities. Define clear policies and procedures to ensure consistent and secure access management. Choose the right IAM solution that fits your organization’s needs, and regularly review and update access rights to maintain security. Providing ongoing user education and training is crucial for ensuring that all users understand and adhere to IAM policies.
By implementing a comprehensive IAM strategy, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Ready to take your IAM strategy to the next level? Try miniOrange IAM solutions for free and secure your enterprise with confidence. Start your free trial with miniOrange IAM.

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products