Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Content Caching is a feature to keep a copy of commonly fetched static content, like images, PDFs, links, and style sheets, for quick calling and faster load speeds in future requests for the same site content. Caching pages and websites help you cut down site load speeds and latency to give a phenomenal increase in website load speed. Caching website data along with site speed also improves performance when there is a sudden increase in network traffic and requests coming to your websites.
Once you know which websites get frequent requests from users, you can store the content for these websites temporarily for a quick lookup service. This is called cached data. With this cached data, you can cut down on your web server loads significantly, and the request-response cycle will improve for fresh users visiting your website. Content Caching also works for Networks, to store static content like images, various media files, certain JS scripts, and many more depending on the user's needs. Browser caching is a type of content caching, where a copy or subset of data is stored in the web browser for a faster load and lookup service for several cached websites. This allows the users to easily and quickly view the cached web pages under your web domain. In certain scenarios, to erase or delete user sessions from a website, you can also Purge Cache, which forcefully erases the server cache stored on the web browser or the network. This is also known as clearing cache or clearing browser cache.
Let’s understand the Content Caching solution with an example. Suppose a high-traffic web server is receiving several requests for an application, from different users.
In this way, by utilizing the feature of caching, the load on the backend servers is reduced by the reverse proxy server, along with increasing the speed of the request-response cycle. The user can specify the amount of time for which the cached content will be valid. After that period, the cached content will be updated.
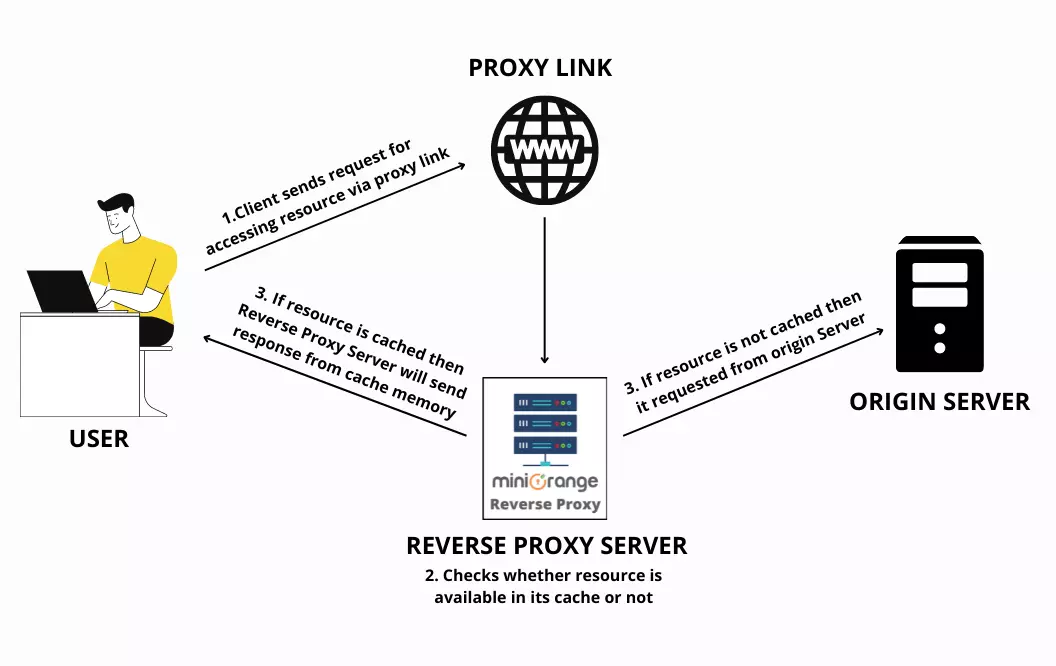
Let’s take the example of one of our customers who configured a Content Caching Solution onto his domain using our product. The client had enabled the feature of caching onto the server.
Suppose a specific site page receives numerous amount of requests from various IP addresses. In such a scenario, the server cache checks whether the user has given the needed permissions for the requested web page to be cached.
If the page has the required cache permissions, it is cached onto the server so if there’s another request that is made for the same web page, the server cache can respond to it directly without having to forward the request to the customer’s server(s) in the backend with fast lookup services and reduced latency.

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products